How to Install MariaDB Easily for Beginners
Install MariaDB by updating your package list and running the MariaDB installation command on your Linux system. MariaDB is an open source database used to store data securely. MariaDB is currently used in huge and well-known companies such as Google, Craigslist, Wikipedia, Archlinux, RedHat, CentOS, and Fedora and is very popular on the Linux operating system. Follow basic setup steps to start using MariaDB. This guide is suitable for beginners.
🤖 AI Overview:
To install MariaDB, you need to follow specific steps that prepare your system for this popular open-source database. The main topic is the installation process of MariaDB on supported operating systems. This involves downloading the correct software packages and using recommended commands to complete the installation. MariaDB is widely used for managing databases efficiently and securely.
Quick Steps to Install MariaDB:
- Update your system packages using
sudo apt update - Install MariaDB server and client with
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client - Start the MariaDB service automatically after installation
- Check MariaDB status by running
sudo systemctl status mysql - Secure your MariaDB setup using
sudo mysql_secure_installation - Set a root password when prompted during the security script
- Remove anonymous users and test database when asked for higher security
- Confirm and reload privilege tables to complete the MariaDB installation process
What is MariaDB
Mari DB is written in C ++, Perl, and Bash and supported in Microsoft Windows, Linux, OS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris operating systems.
In short, MariaDB can be called the optimized version of Mysql because it is much more efficient in performance and also has better security, and is faster in responding to queries. Those who host a large number of websites will really like this database. Usually, sites that work well with Mysql 5.6 and above will work well with Maria DB too.
And there is no need to worry about incompatibility issues after upgrading to MariaDB, and you can safely do so.
In this article, we are going to explain how to install the MariaDB database on Ubuntu 18.04. You can run this database on an online Linux VPS and access it from anywhere!
Install MariaDB On Ubuntu 18
First, we install the MariaDB database with the following command.
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-clientAfter installation, MariaDB services should start automatically. To make sure it is up and running, check its status as below.
sudo systemctl status mysqlMariaDB has no security by default; you need to run the security script below to secure it. You will be asked to set the root password to ensure that not everyone can log in to the MariaDB database.
sudo mysql_secure_installation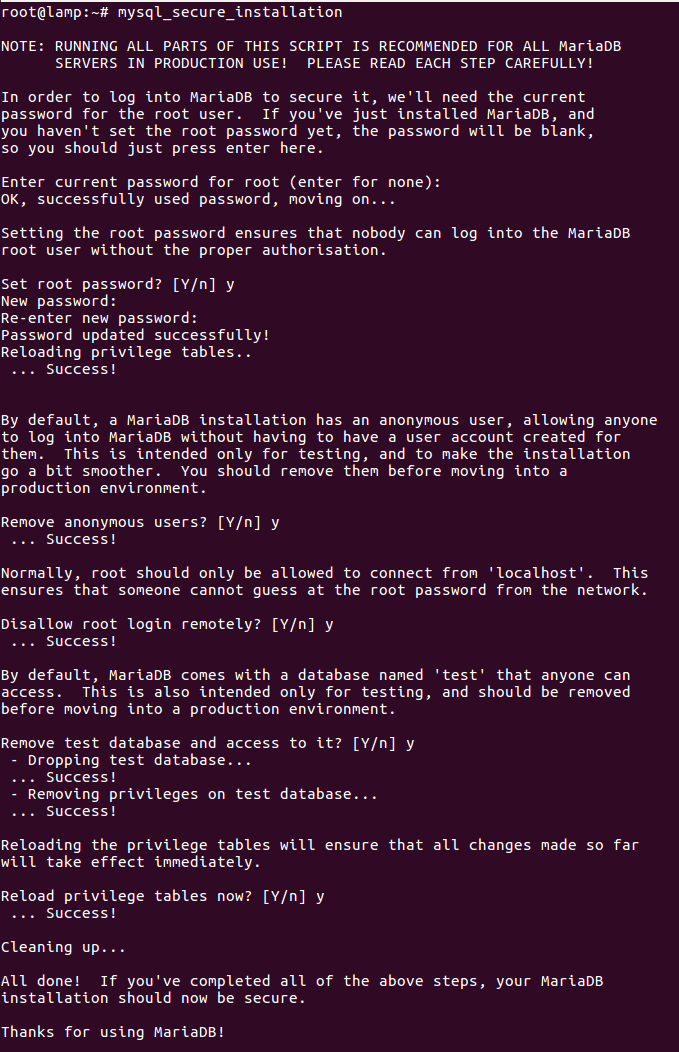
When you run the script, it will ask you to enter the current root password. (do not enter anything and press Enter).
Then enter yes / y to answer the security questions below.
Set a root password? [Y/n]: y
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : yFAQ
How do I install MariaDB on a Linux server?
To install MariaDB on a Linux server, you need to use your system’s package manager. For example, on Ubuntu or Debian, you can use apt. First, update your package index, then run sudo apt install mariadb-server. On CentOS or Fedora, you can use yum or dnf commands instead. Always check the official MariaDB documentation for the latest instructions.
What are the system requirements for installing MariaDB?
MariaDB can run on most modern servers with at least 1 GB of RAM and minimal CPU requirements. For production use, it is recommended to have more memory and disk space depending on your database size and workload. MariaDB supports popular Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Fedora, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
How do I secure my MariaDB installation after setup?
After installing MariaDB, run the mysql_secure_installation command. This script helps you set a root password, remove anonymous users, disable remote root login, and remove test databases. These steps help protect your MariaDB server from unauthorized access.
Can I install MariaDB alongside MySQL on the same server?
It is possible to install MariaDB and MySQL on the same machine but it is not recommended for beginners. Both use similar ports and files, which can lead to conflicts. For best results, choose one database management system to install and use on your server.
How do I access and manage MariaDB after installation?
After installing MariaDB, you can access it using the mysql command-line client. To log in, use mariadb -u root -p and enter your password. You can also install graphical tools like phpMyAdmin or use MariaDB’s native tools for easier database management.
What common errors might occur during the MariaDB installation, and how do I fix them?
Common installation errors include missing dependencies, incorrect repositories, or service startup failures. Ensure your package manager is updated, use the correct repository for your Linux distribution, and check service status with systemctl status mariadb. Review logs in /var/log for more details if issues arise.
How do I uninstall MariaDB if I no longer need it?
To uninstall MariaDB, use your package manager to remove the mariadb-server package. For example, on Ubuntu, run sudo apt remove mariadb-server. Remember to back up your databases before removal if you need to keep your data.
Is it possible to upgrade MariaDB to a newer version after installation?
Yes, you can upgrade MariaDB by enabling the official repository for the desired version and running your package manager’s upgrade command. Always back up your databases before upgrading to prevent data loss.
Where can I find more detailed guides or support for installing MariaDB?
You can visit the official MariaDB website for comprehensive installation guides and community support. Additionally, many Linux communities and hosting providers like OperaVPS offer step by step tutorials and technical assistance for users at all skill levels.