How to Encrypt Disk During and After Installing Ubuntu
In the digital developing world, data security comes first. Sensitive data must be encoded into encrypted to be protected. Encrypt disk in Ubuntu ensures that important data will be saved if the storage fails or is stolen.
You can take several precautions to protect Linux devices from potential security breaches. One of them is to enable full disk encryption Ubuntu. Ubuntu whole disk encryption is possible since it is supported by it. So, you can encrypt disk during and after installing Ubuntu.
As an IT professional or developer, you are certainly concerned about cyber threats increasing. The default configurations selected at initial installation are insufficient to secure your device, and using out-of-date software and unpatched Linux systems can greatly raise the likelihood of a breach. Even though some could contend that Linux is the most reliable and secure operating system, misconfiguration is always risky.
Join us with this tutorial to learn how to encrypt a drive in Ubuntu regardless you have installed it, or you intend to.
Prerequisites for Disk Encryption on Ubuntu
To let this tutorial work correctly, provide the options below and move on.
A Server running Ubuntu VPS.
A non-root user with sudo privileges.
Ubuntu Full Disk Encryption Ideas
The process of transforming plain text data into the unintelligible format known as ciphertext is called encryption. Only with the encryption key can one decipher the ciphertext. The cornerstone of data security is encryption. Disk encryption is one of the many features that Ubuntu comes with pre-installed. To encrypt a single disk partition, several partitions, or the complete physical drive, a unique algorithm is applied. Without the secret key that was used for encryption or a password, the drive cannot be unlocked or accessed.
Full disk encryption (FDE) protects your data privacy by keeping hackers and other bad actors from accessing your hard drive while it’s inactive. Encrypt disk in Ubuntu becomes a crucial security setup as more workers choose to work remotely, whether permanently or through a hybrid workplace. You never know when an employee’s equipment might be lost, stolen, or attempted to be accessed using a bootable live medium.
Hacking physically against Ubuntu Linux is simple. Even though users can password-protect the Grub boot menu, a live system such as a bootable USB installer can still access the file system. Ultimately, the best defense against physical hacking of your Ubuntu system disk may be to password-protect the entire disk. This can also be done while installing Ubuntu.
It is necessary to activate full disk encryption when installing Ubuntu. Unfortunately, the only way to activate full disk encryption is to reinstall Ubuntu Linux. If you have previously installed it, you can only encrypt and mount specific partitions. Enabling full disk encryption from the start is essential, as it protects all areas, including the boot partition and swap space.
Ubuntu Encryption Features
The best and certain result of encrypting a Hard Disk in Ubuntu is to increase your system security. Also, the operating system and all of its files are only accessible to those who possess the encryption key. Encrypt disk in Ubuntu ensures that hackers or state governments are unable to monitor your computer and violate your privacy.
Notes You Should Know Before Encrypting Disk in Ubuntu
Before getting started to learning encrypt disk in Ubuntu, it is good to know some downsides. It will be difficult to access and mount Linux file systems on other Linux operating systems. Also, consider that it is not possible to recover data from these partitions. However, the main point is that a user will fail if they misplace the decryption key.
How to Encrypt Disk During Installing Ubuntu
As we mentioned, there are two options to encrypt disk in Ubuntu; During and after installation. In this part, you will review the process of encrypting drive during Ubuntu installation.
Ubuntu provides LUKS-based whole drive encryption throughout the installation process. Almost every Linux distribution supports the LUKS standard disk encryption specification. The entire block device is encrypted. When choosing a partition scheme during the Ubuntu installation, you have the option to encrypt the drive. Let’s see how to enable full disk encryption while installing Ubuntu:
- Select “Advanced features” from this menu.
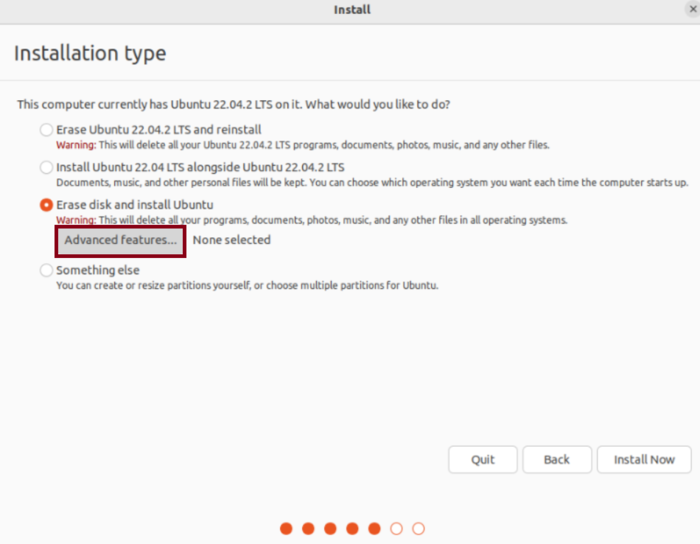
- Select the Use LVM with the new Ubuntu installation from the next window. Then, select Encrypt the new Ubuntu installation for security option.
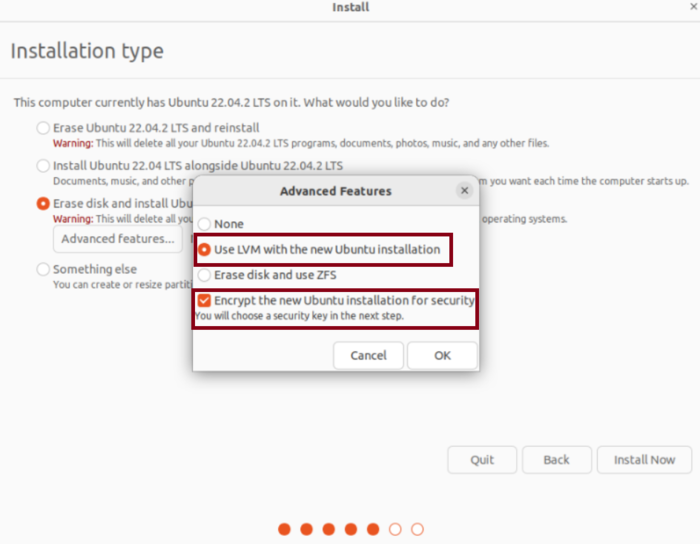
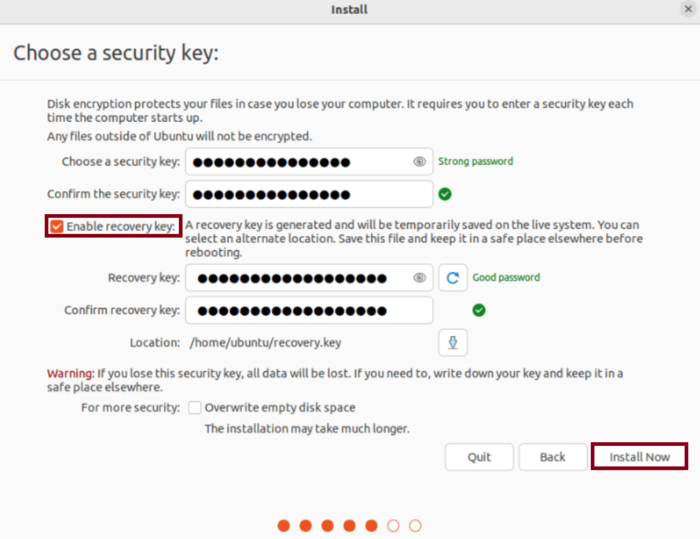
- You are going to need to provide a security key in the following step. While the recovery key can be manually given, it is also created automatically by default. If you forget your security key and need to access the encrypted disk, you can utilize the recovery key.
- The new partition scheme will be shown to you by the Ubuntu installer. As you see below, we chose LVM (Logical Volume Management), hence LVM partitions will be included in the list:
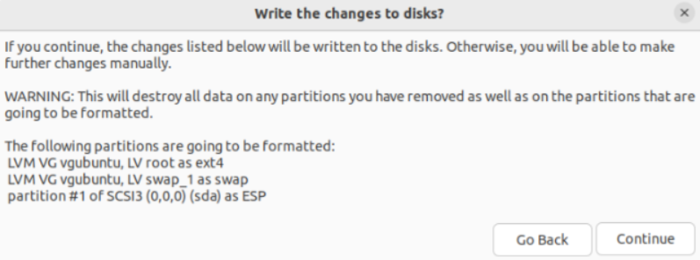
- Restart the computer after completing the remaining installation. You will be asked for the security key on the boot.
How to Encrypt Disk in Ubuntu After Installation
As the second way to encrypt disk in Ubuntu, let’s review Ubuntu encrypt disk after install steps. This option is ideal for users who are running an Ubuntu system and prefer to not reinstall it.
Sensitive information particular to a user is typically kept in the home directory. Data is periodically moved by the operating system between RAM and swap space. Sensitive information may be exposed by abusing an unencrypted swap space. So, to encrypt the disk after Ubuntu installation, you need to encrypt the home directory and the swap space.
- First, you need to install the required packages. Run the following command to install the necessary tools and start the encryption:
$ sudo apt install ecryptfs-utils cryptsetup- Since you need to access another privileged user to encrypt the home directory, you can run the command below and create a temporary user with Sudo Privileges:
$ sudo adduser encrypt-temp- To assign a sudo privileges to the user, type:
$ sudo usermod -aG sudo encrypt-temp- Now, you are ready to encrypt the home directory. Before that, you must log out of the current user and log in to the temporary privileged user by running:
$ whoami- Use the command below to encrypt the home directory of the created user:
$ sudo ecryptfs-migrate-home -u <username>It may take a while, depending on the directory’s size and disk utilization. Following the completion of the process, a set of instructions is displayed.
- Then, run the command below to log out of the temporary user and log back into the original account. This helps you for confirming encryption:
$ whoamiRun the following commands to verify that the read and write operations on the home directory can be completed correctly.
$ echo "the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" > test.txt
$ cat test.txtOnce the data can be read and written, the encryption procedure is considered successful. The passphrase to unlock the home directory is successfully applied after logging in.
How to Get the Passphrase
As an optional action, you can record the passphrase. To do this, run:
$ ecryptfs-unwrap-passphraseGive the login password when prompted for a passphrase. It should show the recovery passphrase on the tool.
How to Encrypt the Swap Space
It’s advised to encrypt the swap space as well to guard against any leaks of private information. But this prevents the operating system from suspending and restarting. All the swap spaces are displayed with the following command:
$ swapon -sThere should be a dedicated swap partition if you choose to use the auto partition feature while installing Ubuntu. The following command can be used to determine the swap space size:
$ free -hThen, encrypt the swap space by running the command below:
$ sudo ecryptfs-setup-swapDelete Unnecessary Items
After a successful encryption process, you can clean up the residuals.
Use the following command to remove the temporary user:
$ sudo deluser --remove-home encrypt-tempTo let the encryption tool provide a backup copy of the home directory of the created user, type:
$ ls -lh /homeAlso, you can delete the backup by running the following command:
$ sudo rm -r <backup_home_dir>That’s it! Ubuntu will no longer be accessible without the decryption key upon system boot.
Conclusion
In this article, you learned How to Encrypt Disk in Ubuntu. Both the explained methods help you to encrypt an entire drive on Ubuntu. You can use any of the solutions according to whether Ubuntu is already installed on your system or not. Linux distributions have done a fantastic job of leading the market and introducing full disk encryption to provide further protection. This has limitations because you are only asked for the password at boot, but it will protect your files and other data. If you are traveling, keep your computer off so that if someone were to intercept your belongings, they would be prompted for a password.
Using this guide, you know how to encrypt the home directory and swap partitions. If you follow the steps of the suggested ways to encrypt disk in Ubuntu, you can protect your important data and system files, but do not hesitate to contact us if you encounter any problems. Our technical support team will try their best to solve your problems.
how to decrypt or remove encryption from home directory can you please update
Dear nagaraju; Here is our best response: Decrypting the entire disk after installation is not recommended, and typically involves reinstalling the operating system without encryption. So, if you are looking to remove encryption, it's best to consult the official Ubuntu documentation for specific instructions on your version.