10 Top Linux Data Recovery Tools for Effective File Recovery
Linux Data Recovery Tools help restore lost, deleted, or corrupted files on Linux systems by scanning drives, recovering partitions, and fixing disk errors. These tools support various Linux file systems and are essential for efficient data recovery.
Here are the Best Linux Data Recover Tools in 2025:
- TestDisk: Partition & File Recovery.
- PhotoRec: File Recovery.
- ddrescue: Data Recovery from Failing Drives.
- Extundelete: File Recovery from Ext3/Ext4.
- Mondo Rescue: Full System Backup & Recovery.
- SafeCopy: Low-Level Data Recovery.
- Redo Backup and Recovery: Full System Backup & Recovery.
- Boot Repair: Boot Issue Fixing.
- Foremost: File Carving.
- Scalpel: File Carving.
Investing in a reliable Linux VPS can provide a stable environment for running these tools, enhancing your data recovery experience.
🤖AI Overview:
Linux Data Recovery Tools are specialized software designed to recover data from damaged, formatted, or inaccessible Linux drives. They employ different methods such as file signature scanning and partition restoration to retrieve valuable files safely and effectively, supporting diverse recovery scenarios on Linux systems.
1. TestDisk
TestDisk is a powerful, open-source data recovery software designed primarily for recovering lost partitions and repairing boot sectors. It supports a wide variety of file systems, including FAT, NTFS, ext2/ext3, and more.
As one of the Linux Data Recovery Tools, it was created to fix issues with non-booting disks, it has evolved to provide advanced data recovery features, such as restoring deleted partitions and making non-booting disks bootable again.
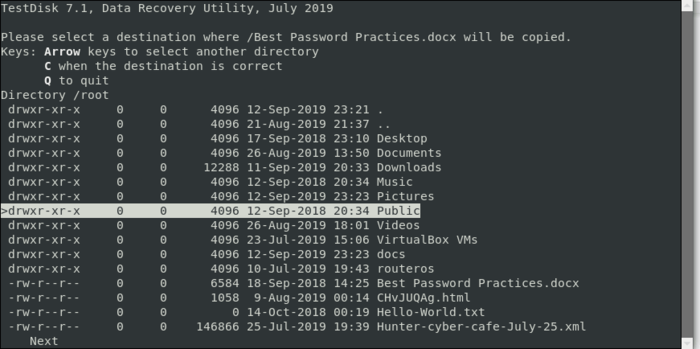
How TestDisk Works?
TestDisk works by analyzing the structure of a disk to locate lost or damaged partitions. It can rewrite the partition table or rebuild the boot sector to restore access.
For file recovery, TestDisk scans the drive to locate lost or deleted files, enabling data recovery from formatted or damaged drives. Additionally, it can rebuild damaged boot sectors, allowing non-booting drives to become bootable again without data loss.
TestDisk Advantages
TestDisk offers several key advantages, including being free and open-source, with regular community updates. It supports a wide range of file systems like NTFS, FAT, and ext2/ext3, making it highly versatile.
The tool excels in recovering lost partitions, a challenge for many recovery solutions, and can even repair boot sectors to restore non-booting drives to a working condition.
TestDisk Disadvantages
TestDisk has a few disadvantages, including its command-line interface, which lacks a graphical option, making it less user-friendly for non-technical users.
Additionally, its advanced features can be complex and require technical expertise to use effectively, which may be challenging for beginners.
2. PhotoRec
PhotoRec is an open-source file recovery tool designed to recover lost files, such as photos, videos, documents, and archives, from hard drives, memory cards, USB drives, and even CD-ROMs.
It works independently of the file system, making it suitable for recovering data from damaged or formatted drives. Though commonly paired with TestDisk, PhotoRec focuses specifically on recovering individual files, rather than partitions.
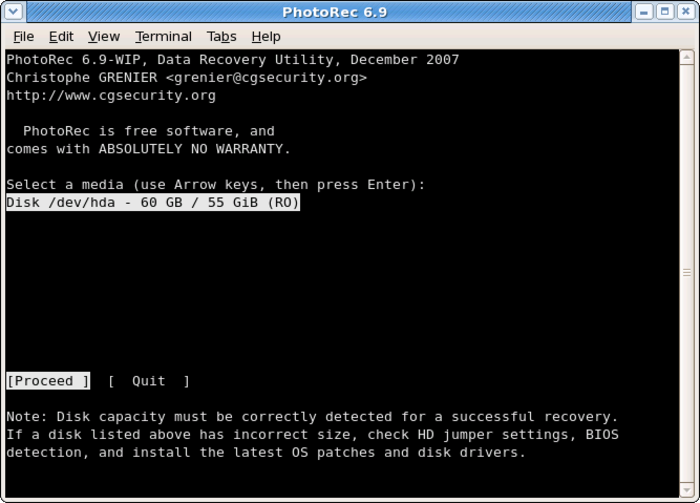
How PhotoRec Works?
PhotoRec operates by focusing on file recovery through a method that bypasses the file system, scanning the disk block by block to retrieve lost files.
It employs file signature recognition to identify file headers, enabling it to recover a wide range of file formats even when the file system is damaged. With support for over 480 file extensions, PhotoRec is versatile in retrieving various types of files from different storage devices.
PhotoRec Advantages
PhotoRec offers several advantages, including being open-source and free, with regular updates from the developer community. It effectively works on damaged or unknown file systems by bypassing them, allowing for file recovery from corrupted or formatted drives.
Its versatility is further enhanced by the ability to recover over 480 different file types. Additionally, PhotoRec is cross-platform compatible, functioning on Linux, macOS, and Windows.
PhotoRec Disadvantages
PhotoRec has some disadvantages, including its command-line interface, which lacks a graphical user interface, making it more challenging for beginners to use. While it can recover files, it does not preserve the original folder structure or file names.
Additionally, PhotoRec is limited to file recovery and does not offer capabilities for partition recovery or disk repair, unlike its companion tool, TestDisk.
3. ddrescue
ddrescue is a command-line-based data recovery tool designed to rescue data from failing, damaged, or corrupted drives.
As one of the Linux Data Recovery Tools, it works by attempting to copy as much data as possible from a failing disk to a healthy one, even in cases where there are bad sectors. The tool is especially useful for recovering data from hard drives that are physically failing or have corrupted sections.
Unlike a simple copy command, ddrescue intelligently skips over unreadable areas and later makes multiple passes to recover data from these sectors.
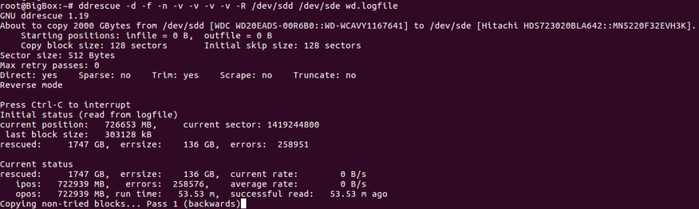
How ddrescue Works?
ddrescue operates in a systematic way to recover data from damaged drives. In the first pass, it copies data from the readable areas of the source drive while skipping over any bad sectors, allowing the recovery process to continue without interruption.
After the initial pass, ddrescue revisits the bad sectors, making multiple attempts to recover as much data as possible from these damaged sections. Throughout the process, ddrescue maintains a log file that tracks the recovery status, enabling it to resume from the last point if the operation is interrupted.
ddrescue Advantages
ddrescue offers several advantages, including its efficiency in maximizing data recovery from failing or physically damaged drives. Its log-based recovery feature allows users to pause and resume recovery tasks, making it highly reliable for extended recovery operations.
Also, as one of the Linux recovery tools, ddrescue is open-source, which means it is free to use and benefits from regular updates from the open-source community.
ddrescue Disadvantages
ddrescue has some disadvantages, including the absence of a graphical user interface (GUI), which requires users to have command-line knowledge, making it challenging for less experienced individuals. It also lacks file repair features, focusing solely on recovering raw data without addressing corrupted files or file systems.
Additionally, its complexity makes it more suitable for advanced users who are familiar with technical operations and low-level data recovery processes.
4. Extundelete
Extundelete is an open-source utility designed specifically to recover deleted files from Linux’s Ext3 and Ext4 file systems. It is a focused tool, meaning it doesn’t attempt to recover partitions or repair disks but concentrates solely on recovering individual files that have been accidentally deleted.
It works by accessing the file system’s journal to retrieve data, as Ext3 and Ext4 file systems are journaled, meaning that they keep track of changes in a log. Extundelete searches through this journal to find information about deleted files and attempts to recover them.
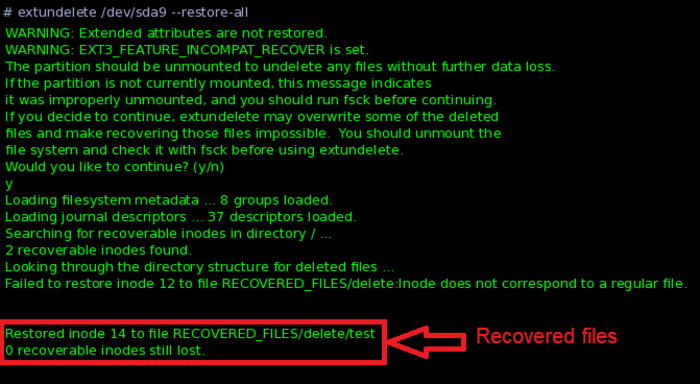
How Extundelete Works?
Extundelete operates by utilizing the journal feature of Ext3 and Ext4 file systems to trace file deletion events. By analyzing the journal, which logs file operations, Extundelete can recover files that have been recently deleted. It further scans the file system’s blocks to locate the areas where deleted data still exists, attempting to restore the data to a new location.
Additionally, Extundelete is capable of performing both partial and full recovery; if the complete content of a file is not recoverable, it can still salvage any remaining fragments to maximize data recovery.
Extundelete Advantages
Extundelete offers several advantages, including its design specifically for Ext3 and Ext4 file systems, allowing for efficient and reliable data recovery on these widely used Linux file systems. Its journal-based recovery method takes advantage of the journaling feature of Ext3/Ext4, making it particularly effective for recovering recently deleted files.
Extundelete is open-source and free, ensuring it is accessible to users and maintained by the Linux community.
Extundelete Disadvantages
Extundelete offers several advantages, including its design specifically for Ext3 and Ext4 file systems, allowing for efficient and reliable data recovery on these commonly used Linux file systems. Its journal-based recovery method leverages the journaling feature of Ext3/Ext4, making it particularly effective for recovering recently deleted files.
Also, as one of the Linux recovery tools, Extundelete is open-source and free, ensuring it is maintained by the Linux community and accessible to all users.
5. Mondo Rescue
Mondo Rescue is an open-source disaster recovery and backup tool designed for Linux and Unix systems. Unlike many recovery tools that focus on individual file or partition recovery, Mondo Rescue creates complete system backups that can be used to restore an entire system after a crash, disk failure, or other disasters.
As one of the data recovery tools in Linux, it supports backing up to a variety of storage media, including hard drives, DVDs, and network storage and can restore data even on different hardware configurations.
How Mondo Rescue Works?
Mondo Rescue works by enabling users to create full or incremental backups of their entire system, which includes all files, partitions, and system configurations. In the event of a system failure, users can boot into a recovery environment using the bootable media (CD/DVD/USB) that Mondo Rescue creates, allowing for the restoration of the entire system from the backups.
It also offers versatile restore options, enabling users to restore systems on new hardware or different disk configurations, making it particularly useful for system migration or repair tasks.
Mondo Rescue Advantages
Mondo Rescue offers several advantages, including its capability to perform comprehensive backups of the entire system, encompassing the operating system, files, and configurations. It is cross-platform, functioning on a variety of Linux distributions and Unix-based systems.
Additionally, Mondo Rescue creates bootable recovery media, facilitating easy recovery even in situations where the system cannot boot, ensuring users can restore their systems quickly and effectively.
Mondo Rescue Disadvantages
Mondo Rescue has some disadvantages, including a complex setup that can make the backup and restore process challenging, as it often requires users to have a solid understanding of advanced Linux concepts. The backup process can also be slow, particularly for larger systems, which may result in significant wait times.
Also, as one of the Linux recovery tools, Mondo Rescue primarily operates through a command-line interface, lacking a graphical user interface (GUI), which can be daunting for non-technical users.
6. SafeCopy
SafeCopy is a data recovery tool specialized for extracting data from damaged or corrupted storage media, such as hard drives, CDs, DVDs, or USB sticks. It works by copying data from a failing source and trying to bypass or recover from unreadable sectors.
Unlike regular copying methods, SafeCopy is designed to handle read errors more gracefully by retrying bad sectors, skipping them temporarily, or using alternative methods to retrieve data. This makes it highly useful for recovering data from physically damaged media.
How SafeCopy Works?
SafeCopy operates by implementing a structured approach to data recovery from damaged drives. It features robust error handling, attempting to read data from damaged sectors multiple times before deciding to skip them, which maximizes the potential for recovery in problematic areas. SafeCopy also employs a multi-pass approach, making several attempts over bad sectors to extract as much information as possible during each pass.
Furthermore, it works at a low level, directly interacting with the drive and bypassing the operating system’s file system checks, enabling it to recover data effectively even from severely damaged media.
SafeCopy Advantages
SafeCopy offers several advantages, particularly its effectiveness in recovering data from physically damaged or corrupted storage devices. It operates at a low level, directly interfacing with hardware to maximize recovery from failing sectors.
Additionally, SafeCopy features flexible error handling, allowing it to skip bad sectors and attempt multiple retries, which enhances the likelihood of successful data recovery.
SafeCopy Disadvantages
SafeCopy has several disadvantages, including its lack of a graphical interface, and operation solely through the command line, which may intimidate non-technical users. The recovery process can be slow, particularly depending on the extent of damage to the media, as it retries reading from bad sectors multiple times.
Moreover, its features are limited to low-level data recovery and do not include options for partition recovery or file repair.
7. Redo Backup and Recovery
Redo Backup and Recovery is an easy-to-use, open-source backup and disaster recovery software designed for both Linux and Windows systems. It focuses on simplicity by offering a graphical interface, making it accessible even to non-technical users.
The tool allows users to create full system backups and restore them in case of data loss, hardware failure, or corruption. It runs from a live CD/USB, meaning it doesn’t need to be installed on the system, and can be used even if the operating system is non-functional.
How Redo Backup and Recovery Works?
Redo Backup and Recovery operates by booting directly from a live CD or USB drive, allowing users to access the tool without relying on an installed operating system. It creates a complete image of the system’s hard drive or specific partitions, storing the backup on external media or network storage.
In the event of a system crash or data loss, Redo can restore the backed-up image, effectively bringing the system back to its previous state, even if it’s being restored to new hardware.
Redo Backup and Recovery Advantages
Redo Backup and Recovery offers several advantages, including a user-friendly design with a simple graphical interface that makes it easy for beginners to perform full system backups and recoveries. Since it runs from a live CD or USB, it does not require installation and can effectively recover data even if the operating system is unbootable.
Additionally, it provides cross-platform support, functioning on both Linux and Windows, which enhances its versatility for recovery in mixed-environment scenarios.
Redo Backup and Recovery Disadvantages
Redo Backup and Recovery has some disadvantages, including a lack of advanced features, as it primarily focuses on basic backup and recovery without options for incremental backups or file-level recovery. The original Redo project has not received major updates in recent years, which may limit its compatibility with newer hardware.
Furthermore, backup destinations are restricted to local drives and network shares, with no support for cloud storage.
8. Boot Repair
Boot Repair is a simple tool designed to fix common boot issues in Linux systems, especially those related to GRUB (the bootloader used by most Linux distributions) or Windows bootloaders.
It is typically used when a system fails to boot due to corrupted boot files, incorrect partition settings, or issues that arise after installing multiple operating systems (dual-boot setups).
Boot Repair is included in a live CD/USB environment, so it can be run even if the operating system itself is unbootable.
How Boot Repair Works?
Boot Repair operates from a bootable live USB or CD, enabling access even when the system cannot boot. With a single click, it can automatically resolve bootloader issues by reinstalling GRUB, fixing file system errors, or updating partition information.
For more complex scenarios, Boot Repair offers advanced options, allowing users to back up boot sectors, change default operating system settings, and repair file systems as needed.
Boot Repair Advantages
Boot Repair provides several advantages, including its simplicity and user-friendliness, making it accessible for users with minimal technical knowledge, as most repairs can be completed with a single click. It operates in a live environment, allowing it to run without needing access to the installed operating system, which is especially useful in emergencies.
Additionally, Boot Repair is effective for dual-boot setups, resolving issues that may arise when using both Linux and Windows and ensuring that both systems can boot properly.
Boot Repair Disadvantages
Boot Repair has some disadvantages, including its limited scope, as it primarily focuses on bootloader issues and does not address data recovery or broader system-wide problems. It may not always be effective, particularly in complex cases such as severe disk corruption, where more advanced tools might be necessary.
Additionally, Boot Repair requires a live environment, meaning users need a bootable USB or CD, which necessitates access to another functioning machine to create it.
9. Foremost
Foremost is an open-source file carving tool used for recovering deleted files based on their headers, footers, and internal data structures. Originally developed by the U.S. Air Force, it is widely used for forensic data recovery.
Unlike traditional recovery tools that rely on file systems, Foremost scans the raw disk data (or disk image) to locate file patterns, making it effective even when the file system is damaged or formatted.
As one of the Linux Data Recovery Tools, Foremost works by searching for specific file signatures, making it particularly useful for recovering photos, documents, and videos from damaged drives or deleted partitions.
How Foremost Works?
Foremost operates by scanning the entire disk for recognized file headers and footers, which help determine the beginning and end of various file types, including JPEGs, PDFs, and MP3s. When it identifies a file through its signature, Foremost “carves” it out from the raw data and saves it to a specified location.
Users also have the option to customize the configuration file to select specific file types for recovery, allowing for greater flexibility in various recovery scenarios.
Foremost Advantages
Foremost is particularly effective for recovering files from damaged or missing file systems, making it a reliable choice in challenging scenarios. Its customizable nature allows users to specify which file types they want to recover, enhancing its flexibility.
Additionally, the tool is fast and lightweight, enabling rapid scans while efficiently using system resources, which is beneficial for larger disk volumes.
Foremost Disadvantages
However, Foremost does have some limitations. It operates solely through the command line, which might be daunting for users without technical expertise. The tool focuses specifically on file recovery, lacking the capability to handle partition recovery or disk repair.
Furthermore, it does not retain folder structures or original file names, complicating post-recovery file management
10. Scalpel
Scalpel is an open-source file carving tool that specializes in recovering deleted files from disk images or directly from storage devices. Designed for forensic analysis, Scalpel focuses on identifying and reconstructing files based on their headers and footers, making it effective even when file systems are damaged or reformatted.
It is particularly useful for data recovery tasks that require precision and speed, enabling forensic investigators and data recovery professionals to extract specific types of files based on user-defined criteria.
How Scalpel Works?
Scalpel is a data recovery tool that employs file signature analysis to identify and recover files. It utilizes a configuration file that defines the signatures of various file types, scanning the raw data of the specified media for these signatures. When Scalpel detects file headers, it extracts the data located between the header and footer, effectively “carving out” the files from the raw data stream.
The recovered files are then saved to a designated output directory, making it easy for users to manage and access the restored data.
Scalpel Advantages
Scalpel offers several benefits, including high customizability, allowing users to modify the configuration file to include specific file types for tailored recovery in various scenarios. It is designed for efficiency and speed, enabling quick recovery processes even when dealing with large volumes of data.
Additionally, Scalpel has a lightweight footprint, making it suitable for systems with limited resources without sacrificing performance.
Scalpel Disadvantages
Scalpel has some drawbacks, primarily its command-line-only interface, which can be challenging for users who are not familiar with command-line operations. It also does not recover folder structures, meaning it focuses solely on file recovery without restoring the original directory structure or file names.
Additionally, Scalpel’s effectiveness is limited by the accuracy of its file signatures; if a file type is not included in the configuration file, it cannot be recovered.
What is a Linux data recovery tool?
A Linux data recovery tool is software designed to recover lost, deleted, or inaccessible data from Linux-based systems. These tools can restore data from damaged disks, lost partitions, or corrupted file systems.
How to Find an Ideal Linux Data Recovery Tool?
When selecting the best Linux data recovery tool, consider the specific type of data you need to recover, whether it’s individual files, lost partitions, or complete system backups as tools cater to different needs.
Evaluate ease of use, particularly if you prefer a graphical user interface (GUI) over command-line options, and ensure compatibility with your Linux distribution and file systems.
Additionally, research the tool’s reputation within the community through reviews and forums to assess its reliability.
By the way, here’s a comparison table summarizing the key features, advantages, and disadvantages of the ten Linux data recovery tools discussed:
| Tool | Type of Recovery | Key Features | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TestDisk | Partition & File Recovery | Restores lost partitions and repairs boot sectors | Free, wide file system support, effective partition recovery | Command-line interface, complexity for advanced features |
| PhotoRec | File Recovery | Recovers files by ignoring the file system | Open-source, works on damaged file systems, supports 480+ file types | No GUI, doesn’t preserve folder structure |
| ddrescue | Data Recovery from Failing Drives | Copies data from failing disks, skips bad sectors | Efficient with failing drives, log-based recovery | Command-line only, no file repair features |
| Extundelete | File Recovery from Ext3/Ext4 | Utilizes journaling to recover deleted files | Effective for recent deletions, open-source | Limited to Ext3/Ext4, command-line only |
| Mondo Rescue | Full System Backup & Recovery | Creates complete system backups | Comprehensive backup, bootable recovery media | Complex setup, slow backup process |
| SafeCopy | Low-Level Data Recovery | Extracts data from damaged media | Great for damaged media, flexible error handling | No GUI, slow recovery process |
| Redo Backup & Recovery | Full System Backup & Recovery | User-friendly, runs from a live CD/USB | Easy to use, cross-platform support | Lacks advanced features, limited storage options |
| Boot Repair | Boot Issue Fixing | Fixes bootloader issues | Simple, user-friendly interface | Limited scope, not always effective |
| Foremost | File Carving | Recovers files based on headers and footers | Works without a file system, customizable | Command-line only, limited to file recovery |
| Scalpel | File Carving | Identifies and reconstructs files based on signatures | Highly customizable, efficient, lightweight | Command-line only, no recovery of folder structures |
What are the most important tips to have a successful Data Recovery?
Provide a section with best practices for data recovery, such as:
- Always try to use recovery tools on a copy of the affected disk if possible, to avoid further data loss.
- Avoid writing new data to the drive you are trying to recover from.
- Create backups regularly to mitigate future data loss.
Can I recover data from a formatted drive?
Yes, many Linux data recovery tools, such as TestDisk and PhotoRec, can recover data from formatted drives. However, the success of recovery depends on whether the data has been overwritten after formatting.
Is it safe to use data recovery tools on Linux system?
Yes, as long as you follow the tool’s instructions carefully. However, to minimize the risk of data loss, it is advisable to recover data to a different drive than the one you’re trying to recover from.
Why the recovery tool does not detect my drive?
To troubleshoot this issue:
Ensure that the drive is properly connected and powered on. Check if the drive appears in the system using commands like lsblk or fdisk -l.
If the drive is failing, consider using tools like ddrescue, which are specifically designed for recovering data from failing disks.
Why files cannot be recovered after running the PhotoRec tool?
To solve this issue:
Ensure that you’re using the correct settings or options in the PhotoRec recovery tool. Check if you’ve specified the right file types to recover. If the drive has been heavily overwritten, recovery may not be possible.
How to Solve recovery tool crashes or hangs during the recovery process?
Check if you have enough system resources (RAM, CPU) available for the tool. Ensure that you’re using the latest version of the software.
If the problem persists, try running the tool from a live USB to avoid conflicts with the installed OS.
How to find the recovered files?
Many tools recover files to a default location, often a separate directory. Check the tool’s documentation for where recovered files are saved.
If using PhotoRec, be aware that it does not retain the original file names or folder structures.
How to recover files after repartitioning?
It may still be possible to recover files after repartitioning, particularly with tools like TestDisk. However, the success rate decreases significantly, especially if the new partitions have overwritten the original data.
Conclusion
Linux Data Recovery Tools provide vital rescue options when faced with data loss on Linux systems. For beginners, understanding the range of tools from file recovery utilities to disk imaging software enables better decisions and preparation for emergencies.
While some tools operate through command lines and require technical skills, others like Redo Backup and Recovery offer beginner-friendly graphical interfaces. Employing proper recovery practices such as minimizing use of affected drives and making disk images improves outcomes.
Above all, regular backups remain the best defense. With this knowledge and the right Linux Data Recovery Tools, users can confidently protect and recover their valuable information.
FAQ
2. How do Linux Data Recovery Tools work?
They scan storage devices at a low level to find lost data by recognizing file signatures or repairing partitions and boot sectors.
3. Are Linux Data Recovery Tools safe to use?
Yes, when used properly, especially by working from copies of affected drives and saving recovered data to different drives.
4. Can Linux Data Recovery Tools recover data from formatted drives?
Many tools like TestDisk and PhotoRec can recover files if the data has not been overwritten.
5. Which Linux Data Recovery Tool is best for beginners?
Graphical tools like Redo Backup are user-friendly; however, tools like TestDisk and PhotoRec require command-line knowledge.
6. Why does my recovery tool not detect my drive?
Check drive connection and power, verify with system commands, and consider using ddrescue for failing drives.
7. What should I do if the recovery tool crashes or hangs?
Ensure sufficient system resources, update software to the latest version, and try running from a live USB environment.
8. How can I increase the chances of successful recovery?
Work on drive copies, avoid writing new data to the damaged drive, and regularly back up important files.
9. Can Linux Data Recovery Tools fix boot problems?
Some tools like Boot Repair and TestDisk can repair bootloaders and partition tables to restore system bootability.
10. Where do recovered files get saved?
Recovered files are saved to specified locations; for example, PhotoRec saves files without original names, so check documentation.