Reset MySQL Root Password in Linux & Windows Systems
Learn how to securely reset MySQL root password in Linux & Windows systems. This process involves stopping the MySQL server, using an initialization file with the password change command, then restarting and verifying access.
🤖AI Overview:
Resetting the MySQL root password on Linux and Windows requires stopping the MySQL server and creating an initialization file with the SQL command to update the root password. After restarting the server with this file, users regain access using the new password, ensuring database security across platforms.
Prerequisites to Reset MySQL Root Password in Linux & Windows
To let this tutorial works correctly, provide the options below.
- Access to a Linux VPS or Windows Server running MySQL.
- An existing MySQL database.
- Administrator privileges on the machine hosting the MySQL database.
- A text editor. (Depending on working on Windows or Linux, Notepad and Vim will be your assistants by default).
- Access to a command-line/Terminal interface
Reset/Change MySQL Root Password in Linux [Step by step]
Let’s go through the required steps of this part to learn how to reset/change MySQL Root Password in Linux. To change the password for the MySQL ‘root’@’localhost’ account on Unix, use the steps below. Modify the instructions to use a new hostname section if you want to alter the root account’s password.
Step 1. Log in as MySQL User
The instructions presuppose that you launch the MySQL server using the Unix login account you typically use to do so. You should log in as mysql before following the steps, for instance, if you run the server using that login account. You can also log in as root, but doing so requires that you start mysqld with the --user=mysql option.
Step 2. Locate the .pid file
Find the .pid File for the MySQL Service. It contains the process ID for the server. Your distribution, hostname, and configuration will all affect the precise name and placement of this file. /var/lib/mysql, /var/run/mysqld, and /usr/local/mysql/data are typical locations. In most cases, the file name ends in.pid and either starts with mysqld or the hostname of your system.
Step 3. Stop the mysqld Server Process
Stop the MySQL server if it is running. Open a command line and run the command below to kill the mysqld process:
kill `cat /mysql-data-directory/host_name.pid`When using the cat command, use backticks rather than forward quote marks. These lead to the kill command substituting the output of cat.
Step 4. Create MySQL Password File
To create the password file, open your preferred text editor and run:
sudo vimNow, add the following line in the file to create a text file containing the password-assignment statement on a single line.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword';Keep in mind that the password should be changed to the one you want to use. Try to use a strong password. Also, be aware that the machine you’re using right now will be able to execute the command. Replace localhost with the correct hostname if you’re connecting to a different machine. Finally, save the file to home/me/mysql-init.
Note: Do not save the file anywhere that other users can access it because it contains the password. Make that the file has rights that allow mysql to view it if you are not logged in as mysql, the user that the server runs as.
Step 5. Start the MySQL Server
Set the init_file system variable to the desired name before starting the MySQL server and apply the changes to the password.
mysqld --init-file=/home/me/mysql-init &At server startup, the server runs the code contained in the file specified by the init_file system variable, updating the password for the root@localhost account. Depending on how you typically start your server, more choices could be required. For instance, before the init_file argument, --defaults-file can be required. Delete /home/me/mysql-init after the server has successfully started. (Step 4)
The new password should now allow you to connect to the MySQL server as root. Restart the server normally after stopping it.
Reset MySQL Root Password in Windows
The MySQL ‘root’@’localhost’ account’s password can be changed on Windows by using the steps below. Modify the instructions to use a new hostname section if you want to alter the root account’s password. Log in as Administrator to your system and follow the below steps to reset MySQL Root Password in Windows.
Step 1. Stop the MySQL Server
To stop the MySQL Server if it is running, first open the box, press the “Windows + R” key and type the below phrase, and click Ok.
services.msc
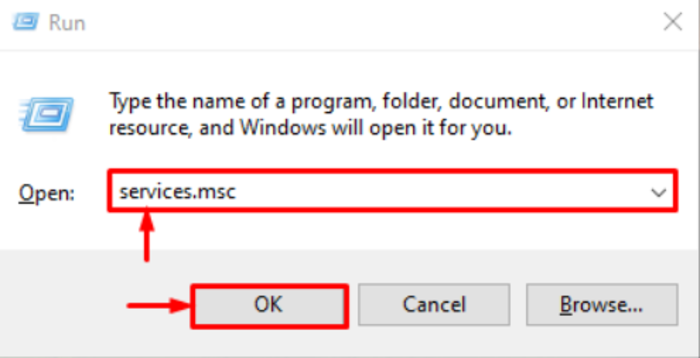
Now, find “MySQL” and select the “Stop” service option.
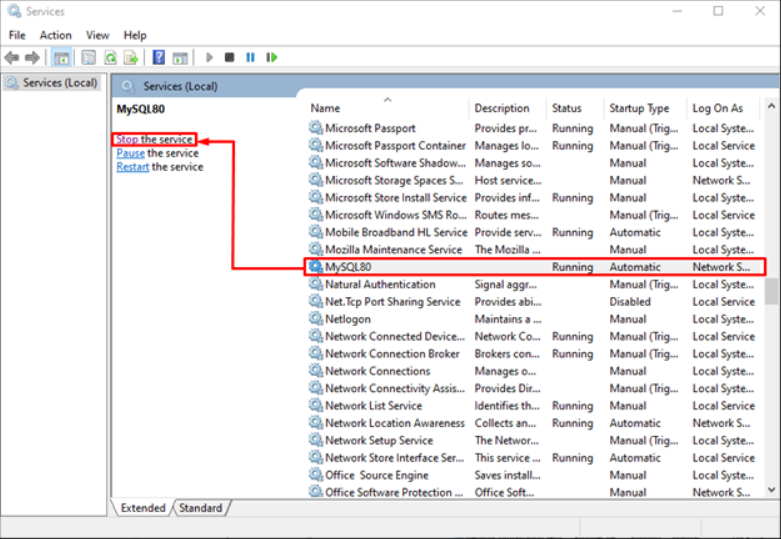
Step 2. Launch Notepad as Administrator
In this step, run the text editor “Notepad” with the “administrator” privileges. To do this, search for Notepad on the menu or use the path below:
menu > Windows Accessories > Notepad.
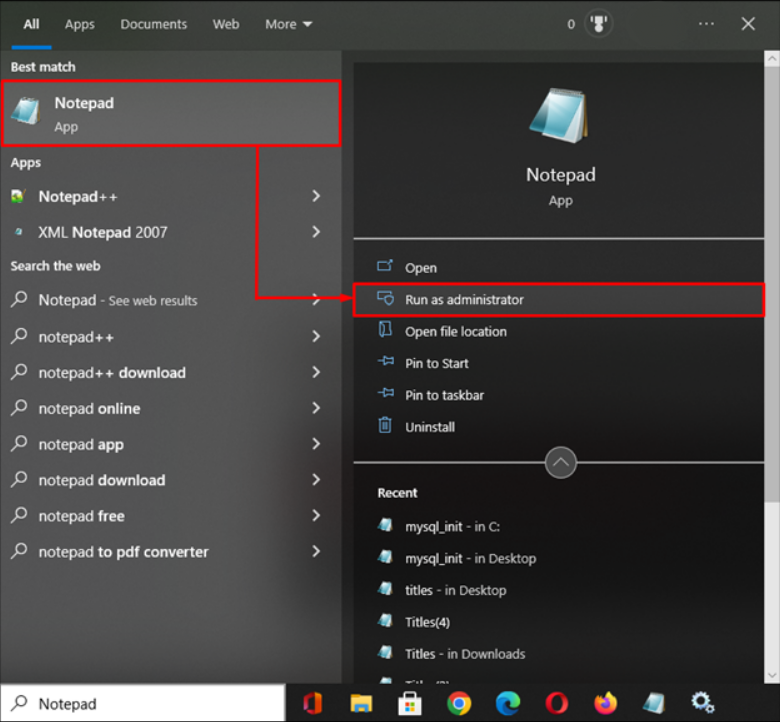
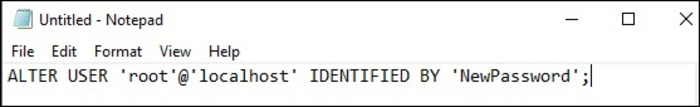
Step 3. Create a New Text File
Into your text editor, type the following line and save the Notepad file.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword';Do not forget to replace NewPassword with the password of your choice.
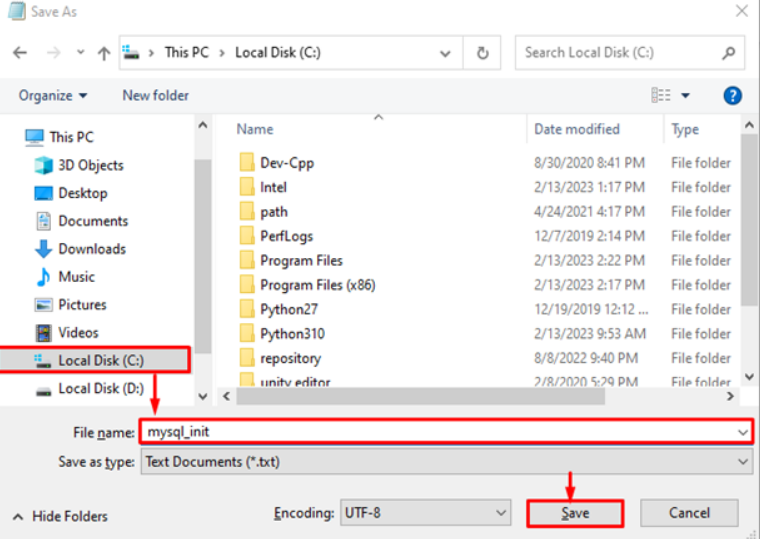
To save the file to the C: drive at the top of your hard drive, use the File > Save As menu. Decide on a filename, like mysql-init.txt.
The localhost command as a result updates the password on your local system. Change localhost to the hostname if you’re changing the password on a system over the network.
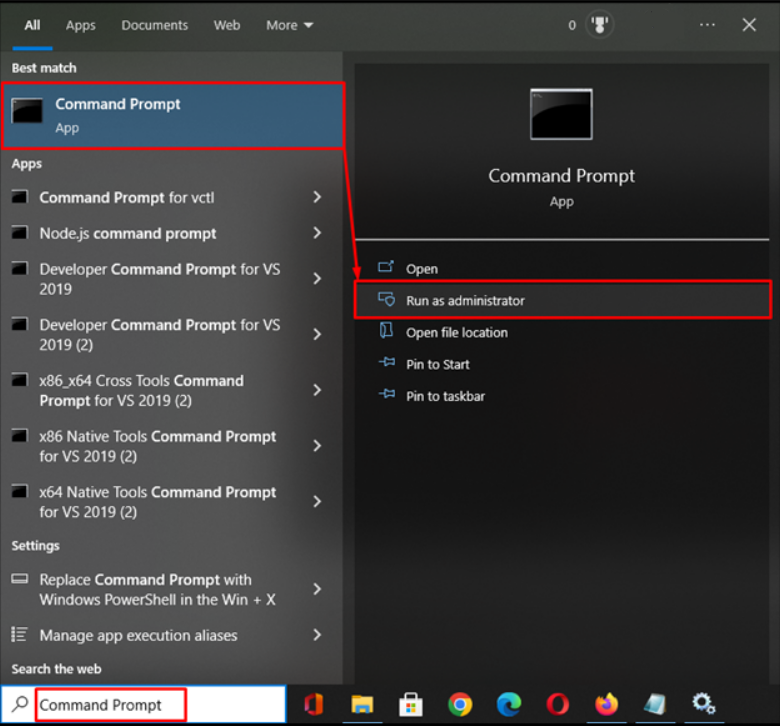
Step 4. Open Command Prompt and Restart MySQL Server
Run the Windows terminal “Command Prompt” as administrator as you see below.
To change the directory to where MySQL is installed, use the “cd” command:
cd "C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin"the text file containing the new password should then be initialized with its destination path before running the “mysqld” command to reset the password. So, enter the following
mysqld --init-file=C:\\mysql-init.txtNow, the user password must be reset successfully, and you can log into your MySQL server as root using the new password.
Note: Use the alternate filename you selected in Step 2 after the double slash.
Step 5. MySQL Reset Password Verification
Run the following command for verification:
mysql -u root -pWhen you confirmed the password change, again delete the C:\mysql-init.txt file once MySQL launches. You’re all done. You reviewed the best and easiest procedure to reset MySQL root password on Windows.
How to Reset MySQL Root Password in Non-Unix/Windows Platforms
Password reset methods are provided in the sections above for Windows, Unix, and Unix-like systems. As an alternative (though less secure), you can reset the password using the MySQL client on any platform by following the below steps:
1. If necessary, stop the MySQL server and restart it with the --skip-grant-tables option. This disables account-management lines like ALTER USER and SET PASSWORD and allows anyone to connect with full rights without a password. If the server is launched using the –-skip-grant-tables option, it also turns off remote connections by activating skip_networking because this is unsafe.
2. Using the mysql client, connect to the MySQL server; Because the server was started using the command --skip-grant-tables, there is no need for a password.
$> mysql3. Tell the server to reload the grant tables in the mysql client for account-management commands to function:
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Then modify the password for the ‘root'@'localhost‘ account. The password should be changed to the one you want to use. Modify the instructions to use a new hostname section if you want to alter the root account’s password.
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass';The new password should now allow you to connect to the MySQL server as root. The server should be stopped and restarted normally (without the --skip-grant-tables option or the skip_networking system variable enabled).
Conclusion
Knowing how to reset MySQL root password in Linux & Windows is a valuable skill for database administrators and users alike, especially when unexpected access issues arise. This step-by-step guide has provided clear methods to accomplish this safely and effectively, respecting security considerations and ensuring continued access to your MySQL databases.
By following these instructions carefully and following best practices, you can maintain control of your MySQL environment even in challenging situations.
If you experience any issues during the process or have questions, do not hesitate to seek assistance from technical support or consult official MySQL documentation. Regularly reviewing your security settings and user credentials will help prevent the need for emergency password resets and protect your data integrity.
FAQ
2. How do I reset the MySQL root password on Linux?
Stop the MySQL server, create a file with the password change SQL command, restart MySQL with this file using the init-file option, then log in with the new password.
3. How is the password reset different on Windows?
You stop the MySQL service, create the SQL command file using Notepad run as administrator, start MySQL from the command line with the init-file option, then verify and delete the file.
4. Why must the MySQL server be stopped to reset the root password?
Stopping the server ensures the password reset command applies safely without interference or compromising data integrity.
5. Can I reset the root password without command line?
Yes, GUI tools like MySQL Workbench offer user management features but access to the server is still needed.
6. How do I protect the password reset file?
Keep it in a secure directory accessible only to privileged users and delete it immediately after use.
7. What should I do if the reset fails?
Check that the MySQL service was fully stopped, verify the file path, and ensure commands are syntax accurate. Consult error logs if available.
8. Are there risks in resetting the MySQL root password?
Risks include exposure of the password file and temporary downtime; following best practices mitigates these.
9. Can I reset passwords remotely?
Password reset typically requires local access to the server or secure remote access with administrative privileges.
10. How do MySQL versions affect the reset process?
MySQL 8.0 uses ALTER USER while earlier versions might require SET PASSWORD or manual user table updates.