Recover Deleted Files in Linux
Have you ever deleted data by mistake and wished to recover the deleted data? Have you ever regretted deleting data? Have you ever had a damaged hard drive and lost important data and regretted it for a long time? You’re not alone, this unpleasant experience is familiar to most users. Now is not the time to grieve for lost data because, by reading this guide, you will learn how to recover deleted Linux files and learn about valuable tools designed to recover deleted Linux files.
The loss of important files may indeed be costly and damaging to you, but Linux does not let sadness remain in your heart because there are various methods to recover data in Linux. It doesn’t matter if your data was deleted a long time ago or recently, by learning how to recover deleted files in Linux using efficient tools such as TestDisk, PhotoRec, Foremost, extundelete, etc., you can get your deleted file data. So don’t be disappointed with your lost data because, by reading this article, your deleted data will be recovered.
How do we recover deleted data on Linux?
Deleting important data is an annoying problem for everyone, and recovering important data is a wish for many users, While this wish has come true. You are lucky to be using Linux, in Linux, it is possible to recover data that has already been deleted or lost for various reasons. This is the reason why users and server managers undoubtedly prefer buying Linux VPS over other operating systems. Linux has many valuable advantages, the ability to recover lost files in the simplest and most varied ways is one of the most important.
Suppose you have accidentally deleted data by pressing the Delete button. In that case, fortunately, the data is not permanently deleted and can be recovered from the Trash section of your Linux distribution desktop environment.
If you have deleted a file by pressing Shift + Del buttons, you should use data recovery tools in Linux, each of which considers different methods for data recovery. Don’t worry that the data will be deleted in Linux immediately when the data is deleted, this does not happen. Even after the data is permanently deleted, it remains on the hard disk partition until it is overwritten. With permanent data deletion, they remain hidden from the file system and are deleted whenever they are overwritten, so there is the hope of recovering data that you have permanently deleted. Configure the partition to be readable but unwritable to prevent accidental overwriting of the hard disk partition containing the deleted files.
You may ask how?
Assume that the data you deleted remains on the /dev/sdb1 partition. To set the partition as read-only, you must unmount the partition and then remount it as read-only. Enter the following commands for this purpose:
sudo umount /dev/sdb1
sudo mount -o ro /dev/sdb1 /media/read-onlyThe partition /dev/sdb1 is mentioned as an example in this tutorial, you should replace the partition corresponding to your system.
clone the partition to another drive is another way to prevent the permanent deletion of important information in Linux. For this, you can run the following command (for example):
dd if=/dev/sdb1 of=/dev/sda1 bs=1MIn the previous example, using the dd command, you were able to clone the contents of the /dev/sdb1 partition in the /dev/sda1 partition.
As a result, you will now be sure that important data on your source partition will not be deleted.
In the following, we will teach how to recover deleted data in Linux through different methods.
Recovering files deleted by Trash in Linux
When data is mistakenly deleted, the first step you can take is to check the contents of the Linux Trash. If you are lucky and have accidentally deleted a file using the Delete button on the keyboard, you can easily recover the deleted data through Trash with a few clicks.
1. First, to run the file manager, right-click on the desktop environment and click “Show Desktop in Files” from the context menu.
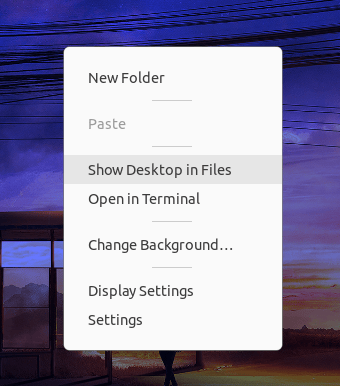
2. On the left side of the screen, find the “Trash” option and open it.
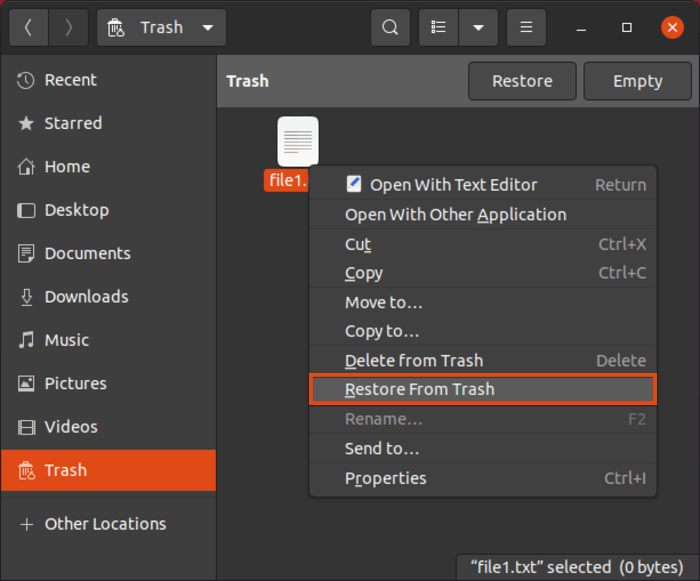
3. After finding the desired file that was accidentally deleted, right-click on the file and select “Restore from Trash “from the drop-down menu to restore the file.
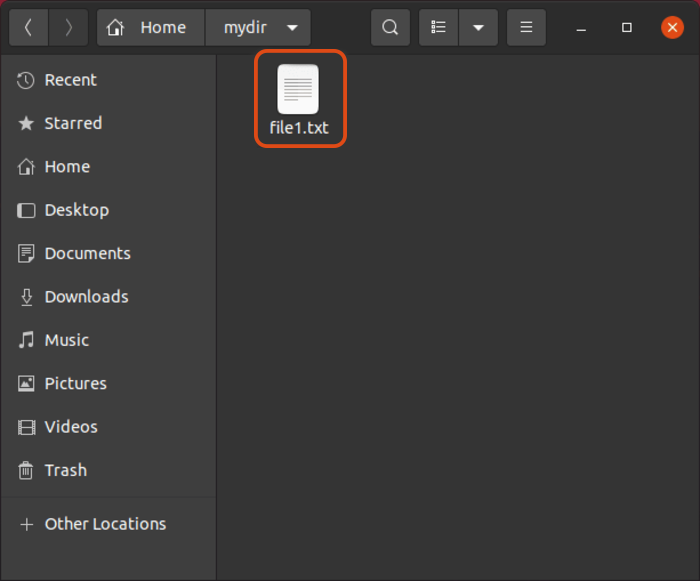
4. As a result, you should find the desired file in the original location.
Recovering files deleted by the TestDisk tool
If you don’t find the deleted file in the Linux trash, it is most likely that you have deleted the desired file either by the rm command or by using the Shift + Delete keys. In this situation, data recovery tools in Linux will help you. TestDisk is a free and open-source terminal-based Linux program for checking and recovering files, data, and partition tables.
As we explained at the beginning of the article, Linux stores files in disk clusters, which are the physical units of data storage. When you delete a file, the disk space occupied by its data clusters becomes available for use by other files. It is possible to use TestDisk to recover deleted files if the disk clusters have not been rewritten.
1. To begin, open a terminal with sudo privileges and type the following command to check if the TestDisk tool is available for your Linux distribution:
which testdisk2. The TestDisk executable path will be displayed if you already have the TestDisk tool installed; otherwise, you can install it with the following command:
- Install testdisk on Ubuntu:
sudo apt install testdisk- Install testdisk on RHEL and CentOS:
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install testdisk- Install testdisk on Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S testdisk3. Run the following command to start the Testdisk tool:
sudo testdiskNote: If you’re launching TestDisk for the first time as a user with Sudo permissions, you’ll be prompted for the sudo password.
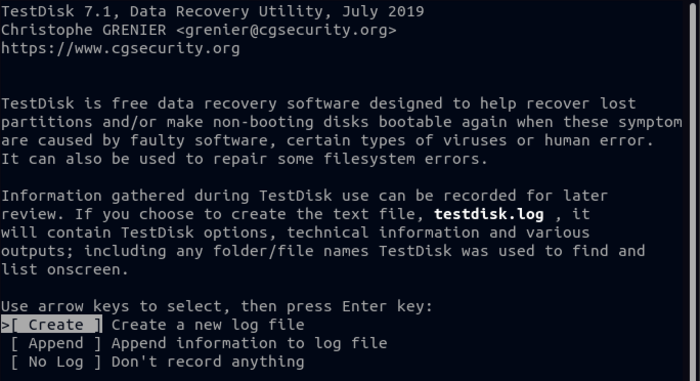
4. After starting TestDisk, TestDisk interactive prompt will be displayed, you can select the options with the help of the arrow keys on the keyboard and then press the Enter button. Select the first option of TestDisk’s initial page(Create option), which is to create a log file, so that your activities in Testdisk are stored in this file. We have already talked about Log file in Linux in detail, you can know more about the uses of LogFile.
5. Here you view all the storage media that are currently attached to your Linux system. You should select the device that contains the deleted files and that you want to recover its data from. After highlighting the desired device, select the” Proceed” option by pressing the right arrow key, and then press the Enter button to select the desired disk or device.
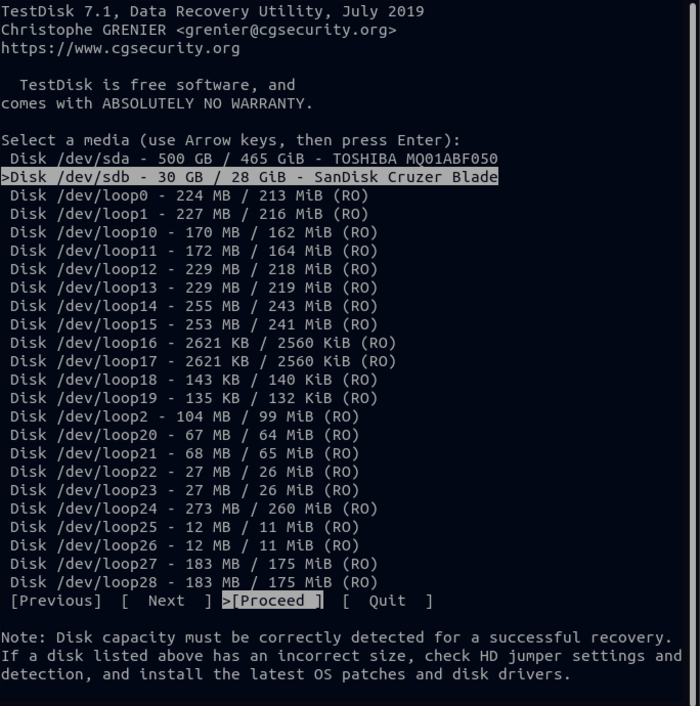
6. On the next page, you must select the disk partition type and press Enter. Since it is not easy to identify the type of partition table, TestDisk will assist you and automatically identify the appropriate partition and specify it.
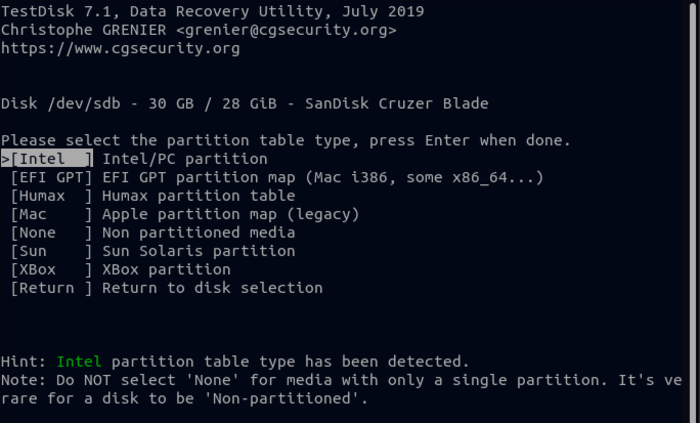
7. In the next step, you will find yourself among different options, you must choose the “Advanced” option to recover the deleted files. In addition to the” Advanced” option, the” Analyze” option is also used to recover deleted partitions, but we prefer the Advanced option. Then press the Enter button.
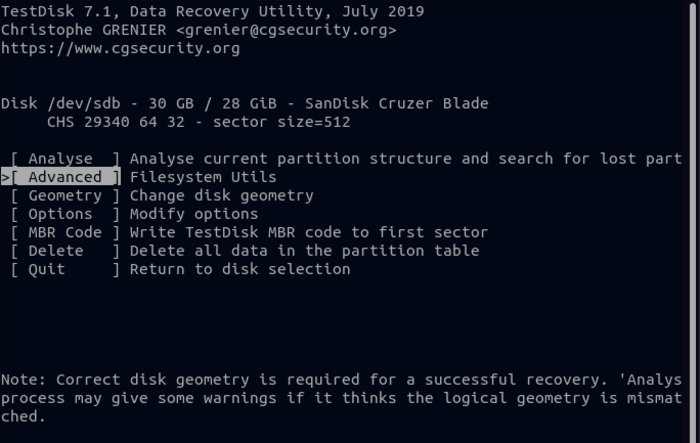
8. You will get a list of partitions on the disk of your choice, you must identify and select the partition that contains the deleted files and select the “Undelete” option in the menu you see and then press Enter. As a result, the files in the partition are identified and a list of deleted files is displayed.
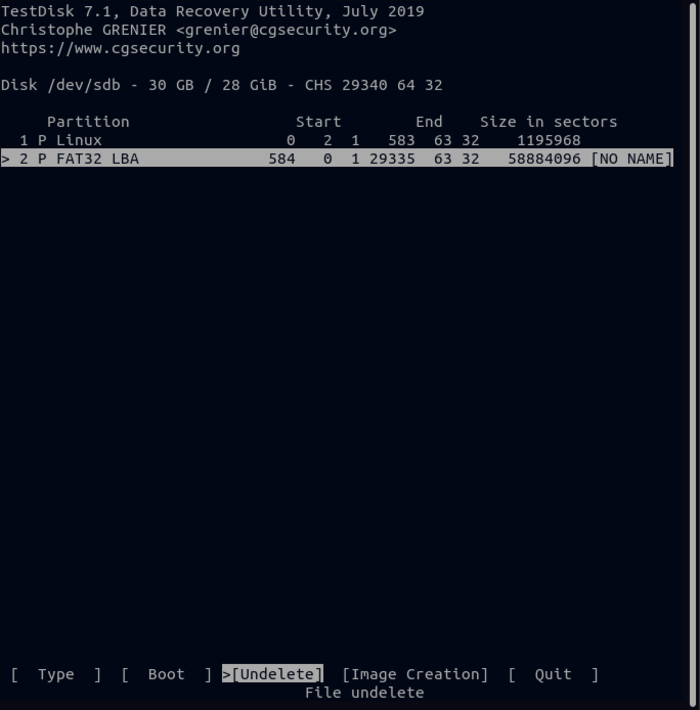
9. Find the file you want to restore in the list and select it.
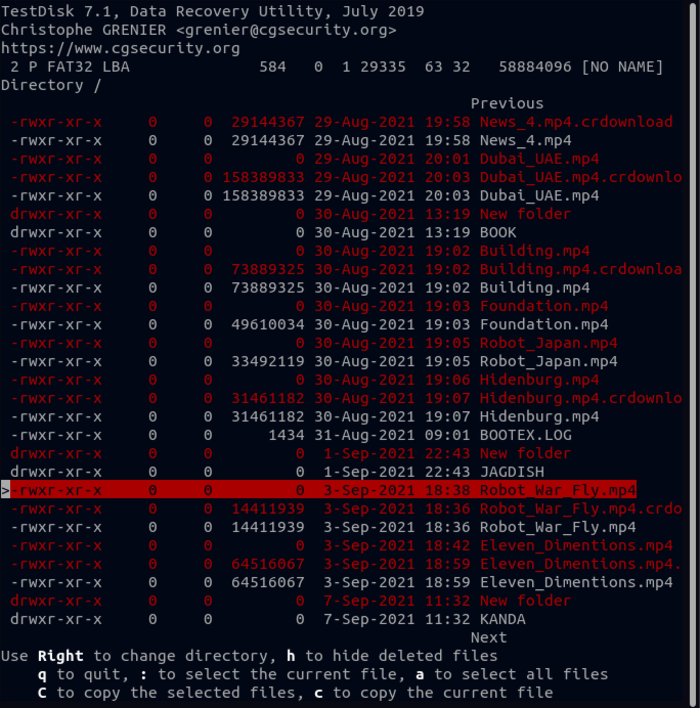
Note: To restore multiple files, when you highlight the file, press the colon (:) key to select the desired file. Also, to select all files, you can press the” A” button and select all files to restore.
10. After selecting the files to recover, press the “C” button to copy your files to the memory.
11. At this step, you will be asked to define a destination to save the file you are restoring and press Enter.
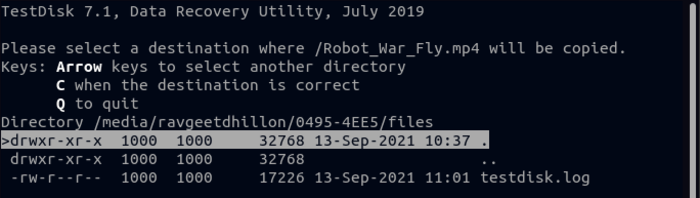
To ensure file recovery, go to the path you specified to save the file and find your deleted file in the specified path.
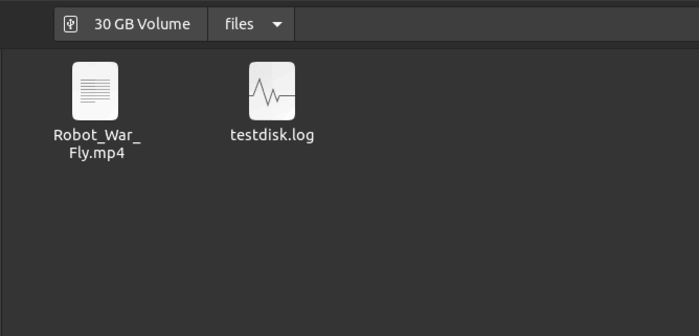
You were successful in restoring the lost data with the help of the Testdisk tool.
Recovering deleted files in Linux by the Foremost tool
Foremost is another efficient and free tool for recovering deleted files in Linux, which provides you with a CLI interface to help you get your deleted data more easily. The Foremost tool is used to recover all types of files, including text, images, videos, and executable files. To use the features of the Foremost tool, follow the steps below:
1. Run the following command to install the Foremost tool on Linux:
- Install Foremost on Ubuntu and Debian:
sudo apt install foremost- Install Foremost on Fedora:
sudo dnf install foremost- Install Foremost on Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S foremost2. After installing foremost, how to use it to recover lost files is not complicated. Enter the following command to access the available options:
foremost -h3. To recover the desired deleted file (for example, picture.jpg file), you can run the following command using the Foremost tool:
foremost -v -t jpg -i /dev/sdb1 -o ~/recovery/The previous command has been executed to search for JPG files in the contents of /dev/sdb1 and recover them to ~/recovery/.
-v flag: used to enable verbose logging.
-t flag: used to specify the files to be searched.
-i flag: used to specify source partition.
-o flag: used to specify the destination directory for saving the desired file.
To recover several different types of files, you can list their extensions using commas.
Recovering deleted files in Linux by PhotoRec
The developers of TestDisk designed another program for data recovery called photoRec. This software was initially designed to recover lost photos, but with improvements, it is now a complete software for recovering all types of files, including documents, archives, and multimedia from hard drives such as hard disks, CD-ROMs, USB, memory cards, etc.
PhotoRec can be introduced as a more advanced tool than Testdisk because it offers more possibilities in recovering deleted data, the ability to identify deleted files through file signatures is one of the advantages of photoRec. PhotoRec has several advantages, but one of its disadvantages is that it does not restore the original filename when it recovers a lost file.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use PhotoRec to recover deleted files:
1. Start PhotoRec: The instructions for installing PhotoRec and TestDisk are the same. If you have already installed TestDisk on Linux, you do not need to install PhotoRec. If the Linux system does not support TestDisk, you can use the PhotoRec features by executing the TestDisk command that we have taught at the beginning of the article. Therefore, start PhotoRec using the following command:
sudo photorec2. Selecting a storage device: After starting PhotoRec, you will see a start menu similar to TestDisk, which displays a list of available storage devices. Select the device from which you want to recover deleted files. You should select the desired disk media using the arrow keys on the keyboard and press the “Proceed” button.
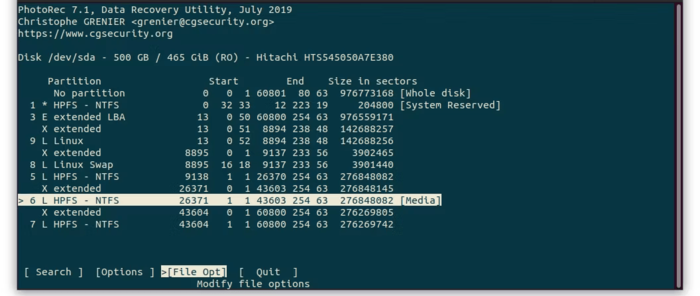
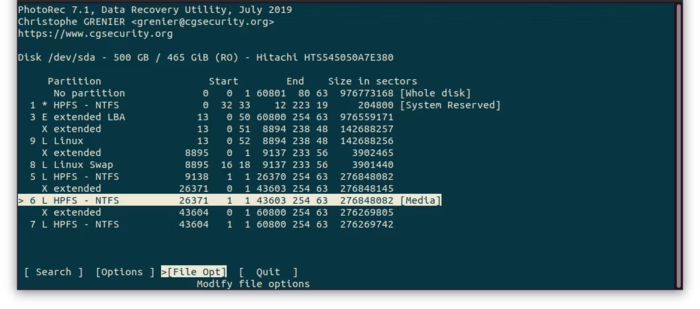
3. Selecting partition: If your storage device has multiple partitions, select the partition where the deleted files were originally located. If you’re not sure, choose the default option that shows the entire device. After selecting the source partition, select the “File Opt” option from the bottom menu.
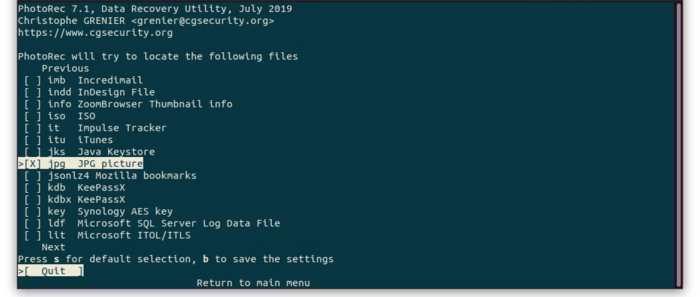
4. Selecting File Type: PhotoRec will ask you to select the types of files you want to recover. You can select specific file formats (eg, JPEG, PNG, DOC, etc.). photoRec selects all types of files by default. To disable PhotoRec’s default setting of selecting all types of files, you can press the “S” button and also press” x” to select a specific type of file. (In this tutorial, We chose jpg as the file type to recover the photo file.)
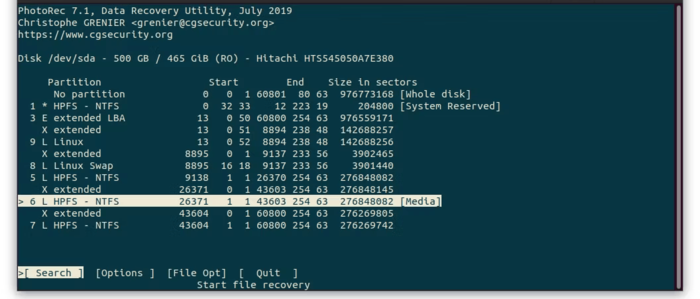
5. Starting the search process: go back by pressing the “q “button and select the” Search” option.
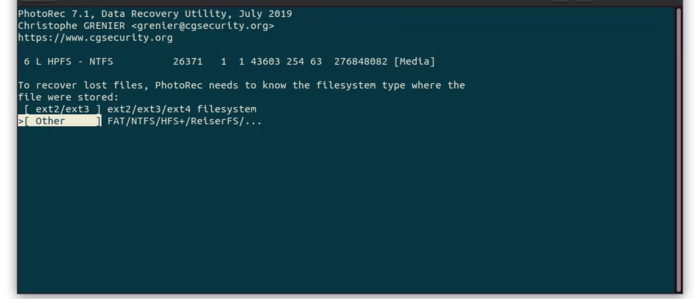
6. Selecting the file system: In the next step, select the type of file system used on the device (such as NTFS, FAT32, exFAT, etc.) or if you are not sure, select “Other“.
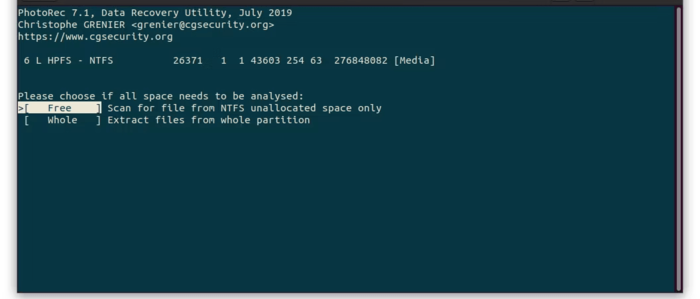
7. Searching for the deleted file in the source partition: In this step, you will be asked to choose between searching the file type in the entire partition and the free space. Choosing the “Free Space “option is more reasonable.
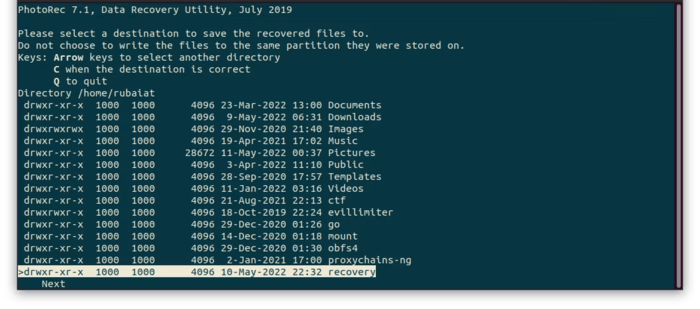
8. Choosing the recovery location: PhotoRec will ask you to choose a destination folder where the recovered files will be saved. To avoid overwriting lost data, choose a different location from the storage device you are restoring. After specifying the desired location using the arrow keys, press the “C” button to save.
9. Starting the recovery process: After selecting the recovery options and the destination folder, PhotoRec will start the recovery process. It will fully scan the selected device and search for deleted files based on their signature and file structure.
10. Waiting for the recovery to complete: Depending on the size of the storage device and the number of deleted files, the recovery process may take some time. PhotoRec displays the progress and number of recovered files in real-time.
11. Review Recovered Files: After the recovery process is complete, you can browse the destination folder you selected earlier to view the recovered files. Remember that the recovered files may have public names and may not retain their original directory structure.
Therefore, using PhotoRec, you can find the deleted files in the directory called recup_dir.
It is important to note that PhotoRec is a powerful open-source data recovery tool, but there is no guarantee that it can recover all deleted files. Recovery success depends on several factors, such as the extent of file fragmentation and whether the space previously occupied by deleted files has been overwritten. To maximize the chances of successful recovery, it is recommended to stop using the storage device immediately after data loss to avoid further overwriting of deleted files.
Recovering deleted files in Linux by Extundelete
Extundelete is a useful open-source command-line tool for recovering files from partitions with the ext3 or ext4 file system. Using the powerful Extundelete tool, the files of the entire directory are also recovered. To recover deleted files in Linux using Extundelete, you can follow these steps:
1. Installing extundelete: If extundelete isn’t already installed, type the following commands in the terminal:
- Install Extundelete on Ubuntu and Debian:
sudo apt install extundelete- Install Extundelete on RHEL and CentOS:
sudo yum install extundelete- Install Extundelete on Arch Linux:
sudo yay -S extundelete2. Partition identification: Select the partition that contains the deleted files. Thelsblkorfdisk -lcommand can be used to see available partitions. The device name and partition number are important(for example, /dev/sda1).
3. Unmount the partition: Ensure the partition is unmounted. Using the following command will unmount it if it is currently mounted(replace /dev/sda1 with the appropriate partition):
sudo umount /dev/sda14. Running extundelete: To get back the lost data, type this command: (change the /dev/sda1 match your partition name):
sudo extundelete --restore-all /dev/ sda1With this command, Extundelete will look for deleted files on the given partition and attempt to recover all of them. –restore-file command followed by the file path or extension is used to recover a specific file from the specified partition. For example:
sudo extundelete --restore-file picture.jpg /dev/ sda1The -o argument allows you to define the output directory; this is useful for saving files to a specific location.
sudo extundelete -o ~/recovery --restore-all /dev/sda1In the previous example, ~/recovery is a special directory that we specified to save the recovered files.
5. Checking for recovered files: The RECOVERED_FILES folder is the folder in the current working directory that contains the files recovered by Extundelete. By checking the RECOVERED_FILES folder, you can be sure of the recovery and saving of the deleted files:
cd RECOVERED_FILES
lsNote: The recovered files might not be in the with the same names as they were before they were deleted.so you may need to manually sort and rename them.
Recovering deleted files in Linux by R-Linux
R-Linux is one of the most popular tools to recover data and files from Ext2/3/4FS file systems, which provides users with a graphical user interface for easier use. In the following, we will provide a guide to recover deleted files by R-Linux:
1. Installing R-Linux: By visiting the R-Tools Technology website, you can download the R-Linux binary file suitable for the distribution you are using. After downloading, install it using the package manager of your operating system.
2. Starting R-Linux: Go to the software menu and find R-Linux and run it. If prompted for a Sudo password, enter it.
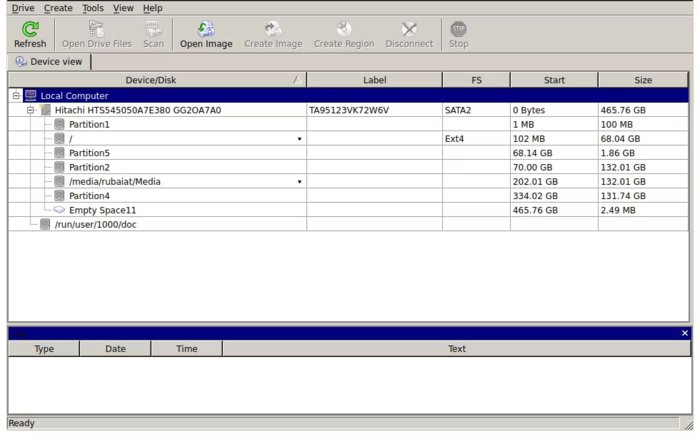
3. Selecting the partition: After selecting the partition where your deleted files are located, scan the partition.
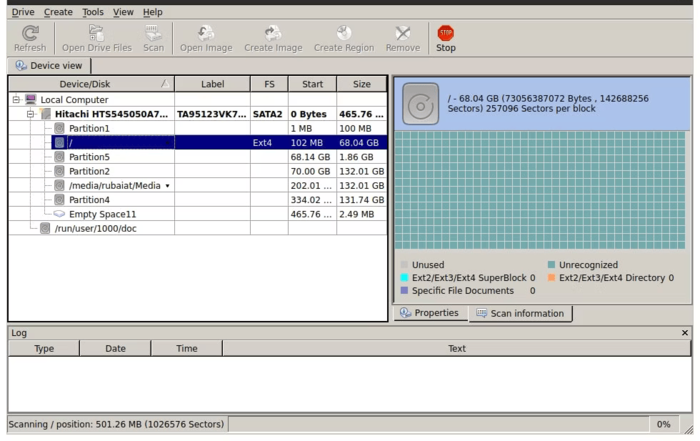
4. After waiting for a while, you will have access to a list of deleted files. Therefore, you select the file you want and recover the file you want from the top bar of the R-Linux tool.
Recovering deleted files in Linux by ext3grep
Using the ext3grep command line tool in Linux, you can scan the ext3 file system to recover deleted files in Linux.
To recover deleted files in Linux using ext3grep, you can follow these steps:
1. Installing ext3grep: Run the following command to install ext3grep:
sudo apt-get install ext3grep2. Identify the partition: Determine the partition where the deleted files are located.
3. Running ext3grep: Run the following command to recover deleted files (replace <drive> with the correct partition):
sudo ext3grep --restore-all <drive>Or
ext3grep --dump-name <drive>To recover special type files, for example, files with .txt extension Run the following command (replace /dev/sda1 with the correct partition):
sudo ext3grep –restore-files “.*\.txt” /dev/sda1
4. Checking the recovered files: ext3grep stores the recovered files in the RESTORED_FILES folder. By checking the contents of the RESTORED_FILES directory, you can ensure that the deleted files are recovered.
cd RESTORED_FILES
lsRecovering deleted files in Linux by ext4magic
If you are looking for the most accessible tool to recover deleted data in Linux, we introduce ext4magic, which is supported by most repositories of Linux distributions. The ext4magic tool provides the possibility of recovering files that are overwritten randomly. Also, by using ext4magic, it is possible to recover the data in the first part of the hard disk that was accidentally overwritten. The ext4magic tool supports all types of files and recovers deleted files by maintaining file permissions, timestamps, and original filenames. Follow the steps below to recover deleted data from EXT4 in Linux using ext4magic:
1. Installing ext4magic: If you haven’t installed ext4magic on Linux before, install it using the following command:
sudo apt install ext4magic2. Identify the partition: Select the partition containing the deleted files.
3. Unmount the partition: If the partition is mounted, unmount it using the following command and having sudo privileges:
sudo umount <drive>4. Running ext4magic: Using the following commands, you can recover deleted files in Linux by ext4magic. (replace /dev/sda1 with the correct partition):
sudo ext4magic /dev/sda1 -r /recovery/directoryReplace /recovery/directory with the path of the directory where you want to save the recovered files.
You can use the following commands to recover data in Linux and add other options to specify file types or search criteria. For example:
ext4magic /dev/sda1 -r -f rajeevedmonds/scripts/purge_cache.sh -d /confidentialIn this example, /dev/sda1 is the disk partition containing the deleted files. purge_cache.sh is a file that was accidentally deleted, and we intend to recover it. We will also specify the main user name (rajeevedmonds) and the name of the directory where the recovered file is stored (confidential) in the command.
Another command used to recover lost data in Linux by ext4magic is as follows:
ext4magic /dev/sda2 -r -f rajeevedmonds/resume.txt -a $(date -d "-6 day" +%s) -b $(date -d "-5 day" +%s)In the previous command, we were going to recover the deleted resume.txt file from the /dev/sda2 partition. Since we did not specify a specific directory to save the recovered file, the recovered file is saved in the /RECOVERDIR directory. In the previous command, we informed the ext4magic command when the file was deleted by specifying the date using the -a and -b flags. (In this example, the file was deleted 5 to 6 days ago.)
Recovering deleted files in Linux by Scalpel
Scalpel is another recovery tool inspired by Foremost. Multithreading on multi-core processors and asynchronous I/O and Regex support are valuable advantages of Scalpel. To take advantage of Scalpel’s features, use the following guide:
1. Installing Scalpel: Install Scalpel by running the following command:
sudo apt install scalpel2. Editing the scalpel.conf file: To recover the desired file, you need to edit the content of the scalpel.conf configuration file. To access the contents of the scalpel.conf, check the /etc/scalpel/ or /etc/ directory, and open the scalpel.conf file and uncomment the line that contains the file extension you want.
3. After saving the scalpel.conf file, run the following command to restore the desired file:
sudo scalpel /dev/sda3 -o recoveredIn the previous command, /dev/sda3 is defined as the disk partition containing the deleted file, and recovered is the destination directory where the recovered file is stored. You can find the recovery directory in the current directory where the command is executed.
FAQ
Why does testdisk sometimes not display the deleted files?
Testdisk is able to recognize deleted files and folders in normal mode. You may have used the List option instead of the Undelete option in the process of recovering deleted files in Linux, which can cause this problem. So make sure to use the Undelete option to identify the deleted files and restore them by following the instructions in our article, and then copy them to the selected folder using shift+c. You also need to change the permissions of the files from root to owner.
How can we recover the data we lost when switching OSes?
The most important thing is to turn off the computer immediately and not load the operating system you just installed until the recovery process is complete. Then you have to boot your computer from the live USB of the operating system you are switching to. Testdisk and photoRec tools help recover deleted data when switching operating systems. We recommend saving the recovered data on external drives.
Conclusion
It is very important to perform the recovery process as soon as possible after accidentally deleting files because if the disk space previously occupied by the deleted files is overwritten, the chances of a successful recovery are reduced. Additionally, it is very important to avoid writing any new data to the partition being recovered from until the recovery process is complete to minimize the risk of overwriting deleted files.
advanced and quality tools to recover lost data in Linux leave no room to worry about the permanent deletion of your important data. By learning how to recover deleted files in Linux, by simply executing a few commands, you can recover data that you lost accidentally or due to hard disk failure. In this article, you learned different methods to recover deleted files in Linux, you can use any method that is easier for you to recover deleted files.
Compared to other tools, TestDisk and PhotoRec are more user-friendly and provide a simple and interactive user interface to make it easier to recover deleted data on Linux. We recommend that to avoid costly and irreparable damage, it is better to regularly make backup copies of your important data on external devices because although these tools are useful in recovering deleted data, they are not always guaranteed solutions to get your valuable data.
If you have another suggestion to recover deleted files in Linux, we will be happy to share it with us and other users.
Related Article : What is Debian OS