Apache vs Nginx: Key Differences for Web Hosting
Apache is an open-source web server that uses a process-based architecture, while Nginx uses an event-driven model for faster static content delivery and lower resource use.
🤖AI Overview:
Apache is an open-source web server used to host websites and manage web traffic. It is often compared to Nginx, which handles connections using an event-driven approach for better speed and lower resource use. The choice between Apache and Nginx depends on specific website needs such as content type and expected traffic.
Apache vs Nginx: A Complete Comparison Guide
As a Network Administrator at OperaVPS, I have often received questions about choosing the right web server. Two names—Apache and Nginx—stand out as leading solutions for hosting web resources. These open-source web servers are trusted by administrators worldwide and serve over 50 percent of web traffic on the internet. However, they are not identical. In this guide, I provide a step by step comparison to clarify their strengths and weaknesses, empowering you to make an informed decision based on your needs.
An Overview of Apache and Nginx
Both Apache and Nginx are recognized for their extensive use and reliability in web hosting. As you seek the perfect web server for your project, it is important to understand that your choice should match your technical priorities and website requirements. This overview assumes you are already acquainted with the basic concept of web servers, as well as with Apache and Nginx themselves.
For the purpose of this comparison, several critical factors will be reviewed, including architecture, performance, operating system support, configuration, security, flexibility, feature modules, customization, and request interpretation. Understanding these aspects will help you identify the differences between Apache and Nginx and select the best web server for your use case.
Detailed Comparison of Apache and Nginx
Stay with me as I explain each important point and why these aspects matter in practical web server management.
| Comparison Point | Apache | Nginx |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Process-driven | Event-driven |
| Performance | Slower | Faster |
| Support | Linux, Windows, macOS | Linux |
| Configuration | .htaccess is used for additional configuration. | Less customizable |
| Security | Secure | More secure |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Less flexible |
| Feature Modules | Several feature modules | Extremely productive modules |
| Customization | More customizable | Less customizable |
| Request Interpretation | Passes File system location | Passes URI to interpret requests |
Apache vs Nginx: Architecture
The network traffic handling method is a major distinction between Apache and Nginx. Architecture shapes how each server responds to user requests and connections, which directly affects website reliability and speed.
Apache uses a process-driven, multi-threaded strategy, where a new thread is created for every incoming request. This basic method may lead to higher resource consumption, potentially reducing server speed during peak traffic.
Nginx implements an event-driven architecture, running a single master process that efficiently manages multiple requests with lower memory and CPU usage. This is achieved through an event loop, allowing Nginx to handle many connections more rapidly.
Apache vs Nginx: Performance
Performance is key for any web administrator. Apache and Nginx differ in handling static and dynamic content, which influences site speed and scalability.
Apache processes dynamic content within each worker instance but can be slower when managing large numbers of requests due to higher RAM usage.
Nginx delegates dynamic content to external processors and is highly optimized for serving static content, often delivering static files two to five times faster than Apache.
Apache vs Nginx: Operating System Support
Support for different operating systems ensures deployment flexibility.
Apache runs reliably on Linux, Windows, and macOS, particularly stable on the Windows platform.
Nginx is also available for Linux, Windows, and macOS. However, it is more stable and preferred on Linux, with some limitations reported on Windows servers.
Both projects provide comprehensive documentation and robust community support through mailing lists, forums, and platforms like Stack Overflow.
Apache vs Nginx: Configuration
Configuration flexibility impacts site management and user access.
Apache allows per-directory overrides with.htaccessfiles, granting non-privileged users authority to control certain settings without full server access. This provides convenience at the cost of some performance.
Nginx does not support per-directory configuration, resulting in faster request processing and a performance advantage, but less flexibility for dynamic user-controlled sites.
Apache vs Nginx: Security
Security is non-negotiable for any public-facing web server.
Apache is secure by design, offering modules like mod_evasive to handle DDoS and brute force attacks.
Nginx further enhances security by using a forward-thinking approach. It disables directory listings by default, limiting unauthorized access, and provides strong SSL support.
Recognizing security measures ensures the protection of website data and user privacy.
Apache vs Nginx: Flexibility
Flexibility determines how easily a web server can be customized and extended.
Apache supports dynamic module loading, making it easy to adapt to changing needs or new functionalities and to install via Docker containers on supported OS platforms.
Nginx can also be containerized but was not initially designed for dynamic modules. An external program is necessary for some dynamic content handling.
Flexibility is especially important for projects that anticipate growth or require frequent modifications.
Apache vs Nginx: Feature Modules
Modules extend web server functionality and influence how thoroughly a server can be tailored to specific web applications.
Apache offers more than 60 official dynamically loadable modules, with many third-party modules provided online. While not all are frequently used, they are available for specialized tasks.
Nginx uses modules that are typically compiled into the server and prioritized for productivity and security. Its module system is lighter but requires advanced configuration.
Apache vs Nginx: Customization
Customization empowers organizations to adapt servers to specific workflows. Meanwhile, choosing the right server for customization reduces future migration efforts and technical limitations.
Apache allows extensive third-party module use, providing tools for URL rewriting, compression, caching, and client authentication.
Nginx requires compiling from source to add non-standard modules, leading to more challenging customization.
Apache vs Nginx: Request Interpretation
How requests are processed determines the effectiveness and efficiency of web traffic handling.
Apache interprets requests based on file system location, which aids in managing both direct and abstract resources.
Nginx interprets requests as URIs, enhancing efficiency and making it well suited for web and proxy server tasks with higher transfer rates.
When to Use Apache Instead of Nginx
Choose Apache when you need detailed control, extensive configuration, high flexibility, and support for low-traffic websites with dynamic content. The ability to use.htaccessfiles and specialized modules allows non-privileged administrators to adjust their own settings easily.
When to Use Nginx Instead of Apache
Use Nginx for high-traffic, secure websites where performance, efficient resource handling, and minimal vulnerability are top priorities. Its lightweight architecture and default security settings offer significant benefits.
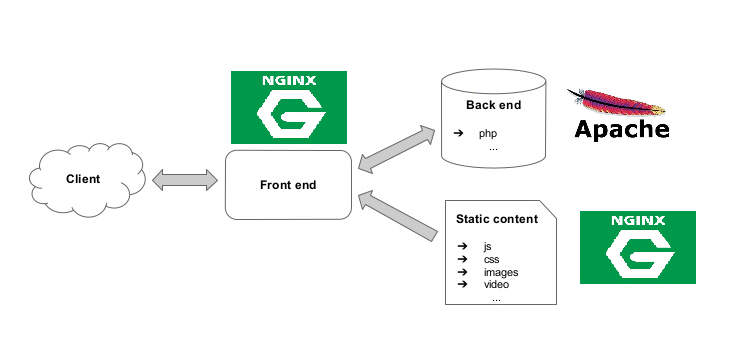
Using Apache and Nginx Together
In some cases, running both Apache and Nginx together lets administrators utilize all the benefits. This setup means you do not have to choose one server at the expense of another’s features. Combining Apache and Nginx can deliver optimal flexibility, security, and performance for complex environments.
Conclusion
This guide covers nine essential differences between Apache and Nginx, summarizing their advantages and limitations for various use cases.
Apache is primarily a web server, while Nginx serves as both a web and reverse proxy server.
Your decision should be based on your project’s needs and priorities. There is no pressure to choose only one—if necessary, you can implement both servers to benefit from their combined strengths.
If you have specific questions or need further guidance, please contact us at OperaVPS for expert support.
Frequently Asked Questions about Apache
What are the main differences between Apache and Nginx?
Apache uses a process-based architecture and allows for per-directory configuration with .htaccess, while Nginx uses an event-driven approach for faster performance and lower resource use.
Which is better for static content, Apache or Nginx?
Nginx is generally faster than Apache for serving static content due to its event-driven design.
Can Apache run on different operating systems?
Yes, Apache supports Linux, Windows, and macOS, making it widely compatible across popular platforms.
Is Apache secure for web hosting?
Yes, Apache offers strong security options, including DDoS protection modules and a well-maintained codebase.
When should I use Apache instead of Nginx?
Choose Apache if you need advanced configuration, detailed user control, or support for dynamic website content with special modules.
Can I use Apache and Nginx together?
Yes, Apache and Nginx can work together, letting you combine their features for improved performance and flexibility.
What configuration options does Apache offer?
Apache lets you use.htaccess files for per-directory settings and provides many modules for customization.
Does Apache support modular features?
Yes, Apache offers over 60 dynamically loadable modules and numerous third-party modules for added functionality.
How does Apache handle web requests?
Apache interprets requests by mapping them to the file system location, allowing support for both direct and abstract resources.