Best Virtualization System To Create VPS
Virtualization is a new solution in computer science and networking that will reduce cost and increase efficiency. Virtualization creates a software layer between computer hardware and software systems, with computer hardware forming the basis for virtual environments. Virtualization systems manage and allocate physical resources such as CPU, memory, and storage to virtual machines, optimizing resource utilization. However, this design is done by considering the ratio of consumer resources.
Virtualization actually gives you the ability to consider a group of servers as a unique resource for computing resources to operating systems. It allows you to run multiple operating systems on one server simultaneously. This means multiple virtual environments can run on a single physical machine, reducing the need for multiple physical computers and simplifying management.
With the knowledge of server virtualization in this article, we intend to examine the differences between several popular virtualizers. Virtualization and cloud computing are closely related, as virtualization is a foundational technology for cloud computing. It enables scalable, cost effective resource sharing and leads to significant cost savings in IT infrastructure.
What Is A Hypervisor in Virtual Machines?
IBM first invented the term hypervisor in 1956 for advanced software programs with RPQ capability on IBM 360/65 computers that shared computer RAM.
A hypervisor is a hardware virtualization model that allows you to run and use multiple guest operating systems simultaneously on a single host system. The hypervisor acts as an interface between virtual machines and the underlying physical hardware, managing resource allocation and isolation.
In this case, virtual operating systems installed, like any real operating system, will use hardware resources in a system such as CPU, Hard or RAM. The hypervisor enables multiple guest operating systems to run on the same physical hardware (host machine).
The hypervisor actually refers to meeting the guest operating system’s hardware requirements and managing the communication between them and how they benefit from the hardware resources. The hypervisor abstracts the underlying hardware resources through a software layer, creating a virtual version of a physical machine for each guest OS.
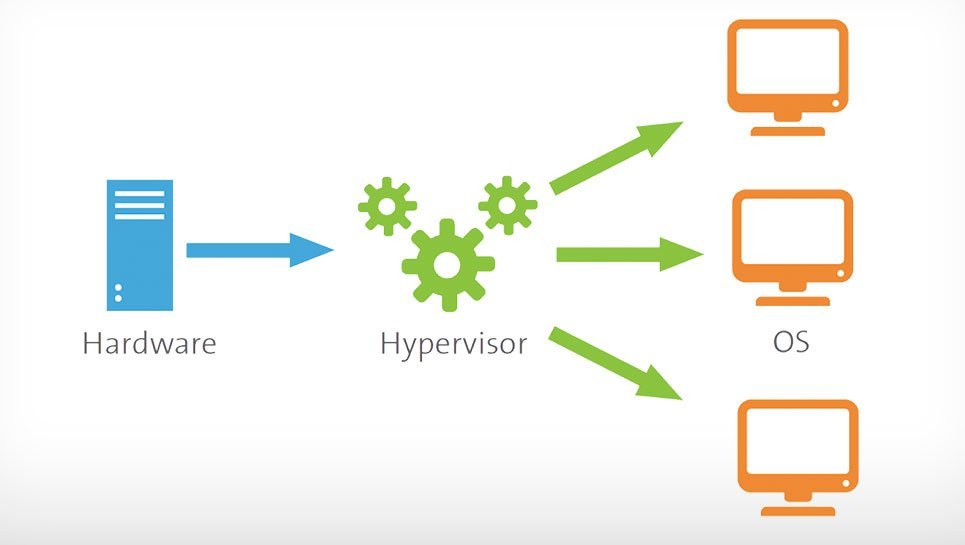
The hypervisor is also called another (VMM), which stands for Virtual Machine Manager, and basically refers to the same subject and does not differ. But in general, there are two types of hypervisors.
- The first type is provided to you as a platform and allows you to install several other virtual operating systems directly by installing them on server hardware. Examples of this type include VMware, ESXi, Citrix, and Xen Server. This type of hypervisor is also called Bare Metal. Both types rely on the underlying physical hardware to provide resources to virtual machines.
- The second type is installed on the host operating system, and you can use it to install and run your guest OS. Both types rely on the underlying physical hardware to provide resources to virtual machines.
What Is The Difference Between Hypervisor Type 1 and 2 for Multiple Operating Systems?
The difference between the first and the second type is that in the second case, the hypervisor is highly dependent on the host OS, which serves as the underlying operating system for the hypervisor. If there are problems with the host OS, other guest operating systems, such as VMware Server, Windows Virtual PC, Microsoft Hyper-V, VMware Workstation will face some issues.
Additionally, operating system level virtualization is another approach, where the host OS is reconfigured to run multiple isolated user environments on a single machine.
Difference Between Server Virtualization Systems
Virtual servers are generally implemented with the help of a virtualization system, using server virtualization software to partition a physical server into multiple virtual servers. Each virtual server can run a separate operating system, providing isolation and flexibility for different applications and services. Virtualization systems also help consolidate multiple servers into a single virtualized environment, optimizing resource utilization and management. In the configuration of these virtual servers, it is considered that the allocation of resources to the virtual server is such that it can operate independently and also prevent disruption for other operators. Virtualized environments offer significant benefits for scalability and efficiency in modern IT infrastructure.
Familiar names for virtualization systems include KVM, OpenVZ, VMWare, Xen.
What Does Virtualization Do Exactly? Benefits of Virtualization
What a virtual maker does is share resources and create separate, independent servers and machines. For example, when installing a virtual machine in a home computer, We can divide that computer’s resources, such as RAM and processor, etc into multiple isolated virtual machines. Virtualization creates multiple virtual environments, each operating independently from the others.
And each of these parts is an individual system with its own operating system. These virtual machines can run different operating systems on the same physical hardware, allowing for flexibility and compatibility. We call these parts a Virtual Private Server (VPS).
They have their own factor, and each can manage their resources individually, without affecting the adjacent machine’s performance. Virtualization allows multiple VMs (virtual machines) to run concurrently, optimizing resource utilization and enabling several virtual machines to share the same physical hardware. When we do the same thing on a server, we will have a virtual server instead of a virtual machine.
If we install a Windows OS on the server, we will call it a Windows VPS, and if we install Linux OS, it will be called a Linux VPS.
Allowing multiple virtual machines and multiple virtual environments on the same hardware provides greater flexibility, scalability, and efficient resource utilization.
What Is Overselling?
In fact, overselling means that more resources are sold to users than the server capacity. For example, if the server has 100 GB of hard drive, there will be no limit on the service sales of one terabyte or more. Overselling occurs when more resources are allocated to virtual servers than the physical server can actually provide. Considering that no user will use all of their server resources, providers offer too many servers.
Overselling usually reduces the quality and performance of the virtual server. This is especially common when multiple servers are consolidated onto a single physical server, which can lead to performance issues. In virtualizers that use this, users can write a lot of input and output on the server on the disk, affecting other users.
However, this often results in less costly service to the user, in which case you can use more resources without paying more. While overselling can lead to cost savings for providers by maximizing the use of physical servers, it may reduce service quality for users. But that’s not the case for medium and large businesses.
Now let’s look at some of the famous virtualization systems.
KVM
KVM (Kernel based Virtual Machine) A virtualization system that is open source and is supported by Red Hat. In this virtualizer, Linux must be part of the central core of the host operating system, but at the same time, there are conditions for setting up a virtual Windows server. KVM enables the creation of virtual machines (VMs), which are software based emulations of physical computers. These virtual machine VMs can run various guest operating systems independently on a single physical hardware system, allowing for efficient resource sharing and scalability.
Since resources are fully allocated to the client in KVM, we will not see overselling
- The disadvantage of KVM: higher cost compared to the OpenVZ virtualizer.
- The advantage of KVM: No overselling and compatibility with Linux and Windows.
OpenVZ
OpenVZ (Open Virtuozzo) is an operating system level virtualization technology for Linux. This virtualizer is also an open source virtualizer that is free, and its installation environment is Linux. It also generally allows the virtual machine to be installed automatically and therefore does not require much technical information.
But in OpenVZ virtual machine, it is impossible to provide a Windows operating system, and only Linux should be used.
- The disadvantage of OpenVZ: Limited to Linux operating system and reduced service quality due to over selling.
- The advantage of OpenVZ: Possibility of automatic installation of the operating system and reduction of service costs and cheapness due to presale.
OpenVZ is not suitable for local desktop virtualization scenarios that require running a hypervisor on a local computer to create and manage virtual machines with multiple operating systems, such as both Linux and Windows.
VMware
VMware is a global leader in the virtualization market. It is a type of BareMetal virtualizer and is commonly used on large, commercial servers. In VMware, more features can be obtained compared to other virtualizers. This virtualizer also has good support. VMware supports application virtualization, virtual desktop, virtual desktops, and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), enabling flexible and secure desktop environments.
- The disadvantage of VMware: High cost.
- The advantage of VMware: No overselling and compatibility with all operating systems.
Xen
Xen is a free and open-source hypervisor developed by the Linux Foundation and originally by Cambridge University, with contributions from companies like Intel. Xen is also a virtualizer of BareMetal and is from the Linux kernel. Xen is widely used by cloud service providers to deliver cloud virtualization solutions, enabling scalable and flexible deployments across diverse cloud environments.
- The disadvantage of Xen: The higher price compared to Openvz and slower than KVM.
Microsoft Hyper-V
Hyper-V is a native hypervisor developed by Microsoft. Hyper-V is one of the largest virtualization products globally, allowing you to virtually use virtual technology to deliver a load of your real environment.
In addition to virtualizing hardware for virtual machines, Hyper-V supports network virtualization, enabling the creation and management of multiple virtual networks and network resources on a single physical infrastructure. This simplifies network management by allowing centralized control and flexible allocation of network resources in virtualized environments.

Hyper-V allows you to present your hardware virtually to have as many virtual machines on your physical system as your hardware supports. Every virtual machine is completely isolated and virtual, no different from a physical system.
Now, in the end, it is you who can answer the question “Best Virtualization System To Create VPS” and take advantage of your desired virtual machine according to the needs as well as the specified budget. If the price is important for you and wants a virtualization system that supports all operating systems, KVM will be the best option. If the price is not the case, then VMware will be the best.
If you want to create Linux VPS, OpenVZ will be the best option. But finally, I think VMware is the best because if you even have a little knowledge regarding virtualizing, VMware will meet your request. After all, it has a user friendly interface.
I hope you have enjoyed this article and found your answer.
Known for being open-source and free to use. It leverages the Linux kernel for virtualization, making it efficient and offering good hardware support.