What is Sudo Essential Guide for Beginners
What is sudo? Sudo is a Linux command that lets authorized users run programs or commands with administrative rights. It helps users perform tasks that need higher access safely.
🤖AI Overview:
What is sudo is a command used in Unix and Linux systems that allows a permitted user to execute specific commands with administrative or root privileges. It is designed to help users perform essential tasks that require higher-level permissions without logging in as the root user. Sudo increases security by limiting access and tracking user actions. This makes systems safer and easier to manage.
What is sudo?
Sudo is a command in Linux that allows you to perform commands with the privileges of another user, most often the administrator. It is especially important when installing software or making system changes, because many actions require higher-level permissions to be completed.
Do You Have To Use Sudo To Run Your Commands?
In this article, I will simply this. If you are using a Root user, it means you have access to all parameters in your Linux server, and you don’t need to use Sudo before each command you write. If you are not using the Root user, this can have two meanings.
- If your user is inside the Wheel group, you can use Sudo before each command to perform administrative tasks.
- If your user is not in the Wheel group, you cannot perform administrative tasks.
What Is Wheel Group?
Only the users inside this group can execute commands with the Sudo command. The Root user is inside the Wheel group.
What Is The Difference Between Su And Sudo Commands?
Su command is used to switch between users in a Linux system where Sudo command is used to execute commands as the administrator of the Linux system.
Should I Use Root User In My Linux Server?
It is not safe to perform commands as a Root user inside Linux servers. Instead, it is better to have a different user in Your Linux VPS Server with root privileges.
In this situation, you will have to use Sudo before each command that you perform.
Example:
$ sudo install nanoDisable Password For Sudo
It is not always easy to do this on each command that you perform because you will be asked to enter your password every time. To fix this, we will add a line in the Sudoer file, and then you will no longer have to enter the password each time you use Sudo.
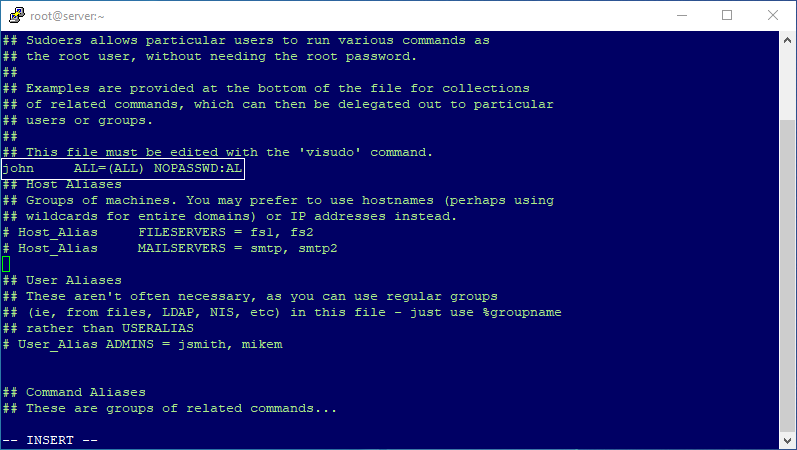
Login to your Linux VPS Server with the Root user and open the Sudoer file using the following command.
# visudoPress Enter button to be able to type and press I to be able to insert the command. Add the following line to any free line and remember to put your username instead of the username parameter.
username ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALLPress Esc, type :wq and press Enter to save your modifications.
If you are still having trouble with sudo, you can refer to our troubleshooting guide about sudo command not found error.
How To Create A User With Root Privileges?
I create the user john, instead of john, write your own username.
Use the following command to add a user.
# adduser johnThe user is now created. Use the following command to add the user to the Wheel group to have Root privileges.
# usermod -aG wheel johnUse the following command to switch to user john. The first time, you will have to set a password for the new user.
# su johnYou can also use the same command to switch to the Root. If you also want to remove the user from the Wheel group, you can use the following command.
# gpasswd -d john wheelHere is what Sudo is. I hope I have explained well and in easy English about what Sudo exactly is. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to ask in the comments section.
Conclusion
Now you know the answer to “What is sudo” and why it is important for system administration and safety. Sudo allows you to perform sensitive tasks securely without needing to log in as the Root user. If you have questions or need more help with Linux commands, feel free to reach out. Your smooth and safe Linux experience matters to us at OperaVPS.
FAQ
2. Why is sudo important for Linux beginners?
Sudo is important because it provides a secure way for you to perform system-level tasks without giving full access to the system. It helps protect your operating system by limiting the amount of time you spend with elevated privileges, which reduces the risk of accidental changes or security issues.
3. How do I use the sudo command?
To use sudo, simply type "sudo" before the command you want to run with administrative privileges. For example, to update your system, you would type "sudo apt update". You may be asked to enter your password to confirm your identity.
4. What is the difference between sudo and the root user?
The root user is the superuser account with unrestricted access to all commands and files on a Linux system. Sudo, on the other hand, temporarily grants regular users administrative rights for specific commands, which increases security by allowing more control over who can do what.
5. Can I control which users can use sudo?
Yes, you can control which users have permission to use sudo by editing the sudoers file. This file defines which users and groups have administrative access and can specify exactly which commands they are allowed to run.
6. What do I do if I get a “user is not in the sudoers file” error?
This error means your user account does not have permission to use sudo. To fix this, a system administrator needs to add your username to the sudoers file or to a group that already has sudo privileges, such as the admin or sudo group.
7. Is it safe to use sudo for every command?
It is best to use sudo only when absolutely necessary. Running commands as an administrator can affect important system files and settings. Always double-check your commands before using sudo to avoid unwanted changes.
8. What should I do if I forget my sudo password?
If you forget your sudo password, you will need help from someone with administrative privileges to reset it. This usually involves booting into recovery mode or using another administrator account.
9. Can I customize what sudo can do for different users?
Yes, the sudoers file allows you to customize which commands a user or group can run with sudo. You can restrict or allow specific administrative tasks to increase security and control over the system.
10. How can I see a history of sudo commands on my system?
You can view the log of sudo commands by checking the system’s log files, usually found in "/var/log/auth.log". This is a useful feature for tracking changes and maintaining security on your Linux system.