How to Fix “E: Unable to Locate Package” Error on Ubuntu
Sometimes, when installing a new package in an Ubuntu VPS using the apt command mentioned below, you may get the following error:
sudo apt-get install package_nameOutput:
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
E: Unable to locate package package_name
The “e: Unable to Locate Package” error means that the OS has not found the package you are looking for.
Spelling the package’s name in the wrong manner or your Linux Ubuntu version being out of date can result in the “E: Unable to Locate Package yum” error.
How to fix Ubuntu 20.04 / 22.04 Unable to locate a package?
Here, we will check and solve every possible reason for the “E: Unable to Locate Package” error.
1. Check the package name
Since Ubuntu is case-sensitive, misspelling the actual package name can cause problems. So, you must pay attention to uppercase and lowercase letters when running commands.
For example, if the file name is “Golang”, typing “golang” will not download the desired package.
Also, note that the package’s name may differ from the name of the software you want; for example, the installable package of “zlib” in Ubuntu is “zlib1g”.
2. Update packages and repository cache
If the cache does not support your desired package, Ubuntu will have problems installing the software and the package.
So, we have to update the package list of the Ubuntu repositories to support new and updated packages and software.
Run the following commands to update the Ubuntu repository packages:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
With the update of Ubuntu repositories, the apt-cache is no longer outdated and supports new and updated packages.
After updating, install the desired package. Try other solutions if you get the Linux unable to locate package error again.
Note: We recommend downloading and installing the packages you need from DEB files. You can remove the lines from the “/etc/apt/sources.list” after installation.
3. Add main repositories to install packages
One of the common problems in old versions of Ubuntu is not pre-installing the main repositories.
Fortunately, this problem does not happen in the newer versions of Ubuntu (such as Ubuntu 20.04 and Ubuntu 22.04) since they are provided along with the main repositories.
If you are using an old version of Ubuntu, add the main repositories for installing packages to Ubuntu by running the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository main
sudo add-apt-repository universe
sudo add-apt-repository restricted
sudo add-apt-repository multiverse
4. Check the availability of the package for the Ubuntu version
If you have tried the previous solutions and your problem is not resolved, it may be that the package you are looking for is not really available for the Ubuntu version you are using.
To find out if the package is available in your Ubuntu, you need to get the complete information about the Ubuntu version by running this command:
lsb_release -aOutput:
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS
Release: 22.04
Codename: jammy
As the command’s output shows, the version of Ubuntu we are using is 22.04.1 LTS with a jammy codename.
Your Ubuntu version may differ from ours; however, you should now look for packages for your Ubuntu version by visiting the Ubuntu Packages official website.
On the official Ubuntu website, scroll down to find the search section. Type the name of the package you want to download in the “Keyword” field.
Then, select the code name from the “Distribution” menu and set the section to any. Finally, click on the search button.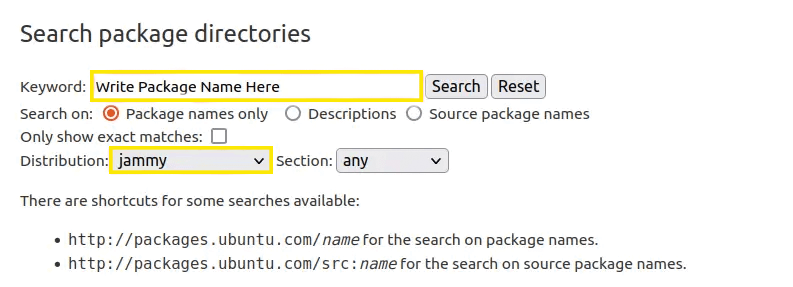
The output will demonstrate whether the package you want to install is available for your Ubuntu version or not. If the desired package is available, check the repository to which it belongs.
If the package is in the universe or multiverse repository, but these repositories are unavailable in the Ubuntu system, you will see the error “E: Unable to Locate Package” again.
Therefore, as in Solution 2, you need to add the relevant repositories to Ubuntu:
sudo add-apt-repository universe multiverseNow, to notify these repositories of new packages, you need to update the repository cache with the following command:
sudo apt updateSometimes, the software is no longer updated, and new versions of Ubuntu do not support the packages of that software.
You can use third-party repositories like PPA to install such software.
If there is no official PPA for the desired package, you can still install it with alternative methods, such as using DEB files or snap packages by checking the official Ubuntu website.
5. Check the activation of the Ubuntu version
If you use the regular version of Ubuntu, you must update the Ubuntu every nine months, and for the long-term version, every five years.
If the Ubuntu version is not supported and has expired, you will receive the error “E: Unable to Locate Package” when installing new packages.
To check the status of the Ubuntu version and ensure that it is supported, run:
hwe-support-status --verboseOutput:
You are not running a system with a Hardware Enablement Stack. Your system is supported until April 2025.The output will display the date until when your system receives active support.
6. Fix the repository
Ubuntu’s “source.list” file contains all repository-related data. The source lists are in charge of tracking down the requested package from the repository for installation.
When you fail to install a package using the apt command, you can check the apt source list to locate the packages.
The apt command looks for the available packages using the source list in the “/etc/apt/sources.list” file. Therefore, open the file with sudo privileges in a text editor and find the following lines:
# deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main
# deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main
After ensuring that the distro’s official source repositories are added, you can get a list from the official mirrors on the distro’s site.
As we can see, both lines have been commented out. This means that apt cannot find packages because there are no source repositories available.
So if apt doesn’t use the source repository to search for packages, we comment or remove the above lines in the file. To see how it would look without the comments, we uncomment both lines:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main
deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main“E: Unable to Locate Package” reasons
There are several reasons for receiving this error, including:
- Misspelling the package name
- The repository cache is out of date
- Desired Package is not available for your Ubuntu version
- Your Ubuntu version is not active or supported anymore
- There is a problem with the resource list
- The main repositories to install the desired package are not available
How to fix unable to locate package git
Some errors are almost the same regarding the ways to solve them. The previous solutions can solve the following errors on Ubuntu, Debian, and Kali.
For instance, you can update the repository cache by this command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yThe errors are:
- unable to locate package sudo
- unable to locate package git
- e: unable to locate package net-tools
- unable to locate package yum
- unable to locate package wget
How do I find the location of a package in Linux?
Installed software is usually located in bin folders like “/usr/bin” or “/home/user/bin”. Also, you can easily locate packages using multiple commands in Ubuntu:
find / -name filename 2> /dev/nullwhich filenameThese commands search and find the location from where the file executes.
FAQ
What should we do if none of the solutions solve the "E: Unable to Locate Package" error?
If you need a software that is not supported by the official and default Ubuntu repository, installing PPA repositories is one of the solutions.
The Ubuntu Launchpad website is useful for searching for packages and their PPAs.
If you don't find the PPA of the package you want on the site, check the official Ubuntu website to use alternative methods to install the software you want.
Can all Ubuntu versions use this article's commands?
All the provided solutions in this article are for Ubuntu 20.04 and Ubuntu 22.4.
Since the newer versions of Ubuntu have received many updates, the way of executing commands may have changed for different purposes.
If you are using a later version of Ubuntu, check whether the commands provided in the new versions have the same functionality as the old versions.
How can the repositories issue be resolved?
The “sources.list” file contains information about repositories in Ubuntu, so to solve the problem, we will restore the default repositories by entirely removing the sources.
Remove the list files from the “/etc/apt” directory and generate new sources.
What is the e unable to locate package netstat error in Ubuntu?
This error indicates that the required net-tools package, which includes the netstat executable, is not installed on the system.
You may need to manually install the net-tools package if it is not already installed on your system.
Conclusion
Getting the “unable to locate package sudo” error is one of the most common errors when installing some packages in Ubuntu.
The immediate solution is to check the spelling of the package name when installing it through the terminal.
We also provided five additional solutions to fix the “e: unable to locate package net-tools” error.
Related Service : Buy Linux VPS