List User in Linux Step by Step Guide for Developers
List User in Linux refers to the process of displaying all user accounts on a Linux system. Use the cat etc passwd or the getent passwd command to list users efficiently. This is essential for managing permissions and access.
🤖AI Overview:
List User in Linux refers to the process of displaying all user accounts present on a Linux system. The intent is to help users or administrators quickly see which user accounts exist for management or security purposes. This can be done using specific commands within the Linux terminal, providing a clear overview of system users.
prerequisite
To be able to list the users connected to a Linux system by the commands that we will explain below, you must first have a system that runs the Linux operating system or you should buy Linux VPS and then manage the users through the commands that we will teach.
- Linux system
- Access to the command line
How to list user Linux (Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS)
There are two types of users in Linux systems: regular users and system users.
System users: Some users are created by the system to run processes that need to run in the background. These users are non-interactive and do not need to communicate with other users to perform their tasks. For example, the root user who has administrative permissions is known as the system user.
Normal users: are human users that the root user has created by granting the necessary permissions. Normal users have a home directory and a login shell to store their files.
In Linux, the /etc/passwd file contains user information, including user UID (identification number), user name, and information about the login shell and the main directory. To manage users, this file must be accessed, and then administrators can list the users based on the information in The /etc/passwd file.
We will guide you through different commands to list the users connected to a Linux system, in this tutorial we will use the following commands:
- The “cat” command
- The “awk” command
- The “compgen” command
- The less and more command
- The “getent” command
- The” grep” command
First Method : Using the “cat” command to list user in Linux
This method is the easiest way to access the contents of the/etc/passwd file and list users.
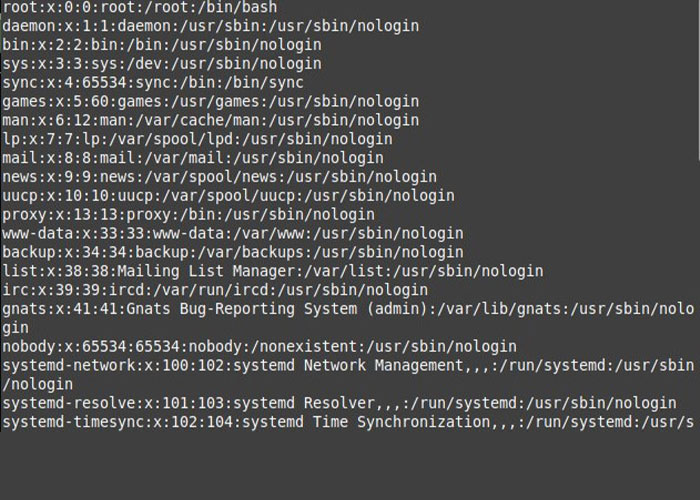
First, enter the terminal environment of your Linux system and execute the “cat” command to access comprehensive information about passwords and usernames stored in the /etc/passwd file.
$ cat /etc/passwdBy executing this command, you will get a list of passwords and usernames along with complete information.
You can use the following command to view the number of users:
cat /etc/passwd | wc –lThe wc command provides you with the statistics of the number of users, and you can find out the number of users by counting the lines you receive in the output.
Second method: using the “awk” command to list users
In this method, the “awk” command displays usernames without additional explanations and more details. This command is useful for administrators who do not need more information about users that is provided in the output of the “cat” command. The syntax of the “awk” asks for the first field in each output line in the /etc/passwd file because the data fields in the /etc/passwd file are separated from each other by the colon symbol.
Therefore, enter the terminal environment and run the following command to view usernames:
$ awk –F: ‘{ print $1}’ /etc/passwd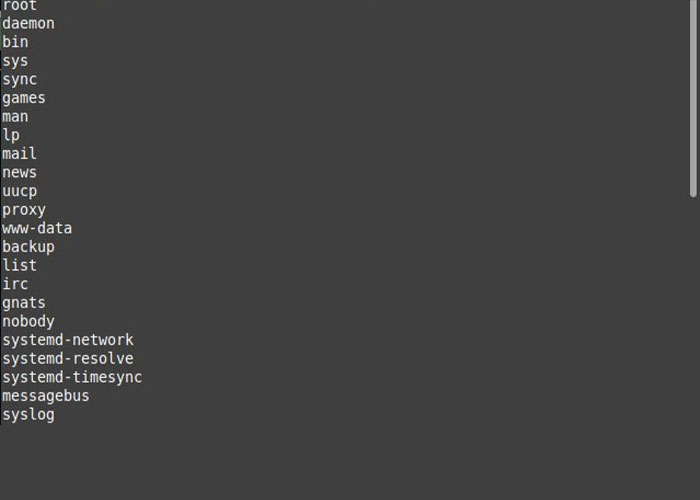
Also, the following command to view the results page by page can be useful for better management:
awk -F':' '{ print $1}' /etc/passwd | lessThe third method: using the “compgen” command to list users
The output of this command is the same as the “awk” command, and you can access only the usernames stored in the /etc/passwd file by executing this command. Therefore, to view usernames, type the following command in the command line:
$ compgen –uFourth method: List users using Terminal Pagers
This method is used for situations where the administrator has to control many users and limit the output of the /etc/passwd file and better review the contents of the /etc/passwd file; In this situation, the command terminal pager (Less and more) is the most efficient way to manage a large number of users.
If you want to use the less command to review the contents of the /etc/passwd file, you must enter the following command:
less /etc/passwdThe output will contain the first page of the file, which you can navigate in the file using the keyboard and view the available data.
The more command also displays the same result as the command above, but this command has more limitations in functions:
more /etc/passwdFifth method: List users using the “getent” command
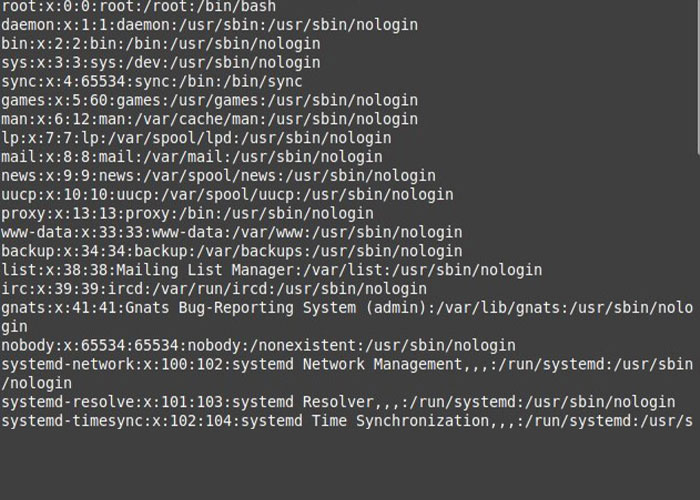
By executing the “getent” command, like the “cat” command, you can access more details.It usually checks system database entries and displays complete information about system database entries by looking up the database stored in the /etc/nsswitch.conf file, which by default The passwd database is saved.
Enter the following command to list the information in the passwd database:
getent passwdThe output of the above command is almost identical to the output of the “cat” command, which provides complete details of the users on your Linux system.
The “getent” command can also help you find specific users. For this purpose, type the following command:
getent passwd [username]The display of the corresponding passwd input line command indicates the existence of the desired user.
Also, in the passwd database, you can search for the UID by executing the getent command:
getent passwd [UID]In the output, the user input with the specified UID is displayed.
If you want to search for users in a specific range using the getent command, enter the following command:
getent passwd {[first-UID]..[last-UID]}The output of the above command displays the users with UIDs that are in our defined range.
sixth method: List users using the grep command
As we introduced you to the types of Linux system users at the beginning of the article, you know that normal and system users each have their unique UID so that you can distinguish them from each other.
The UID of system users is in the range of 0 (root user) to 999 and from 1000 onwards belongs to normal users and new users are given the smallest UID that has not been used yet.
If you want to access the /etc/login.defs file to check the UID range of normal users, enter the grep command:
grep -E '^UID_MIN|^UID_MAX' /etc/login.defsWith the help of the output of the above command, you can find out the UID range for a normal user because it displays the smallest and largest UID that a normal user can get.
Conclusion
Listing users in Linux is a critical task for effective system management and security. By following these steps, developers can reliably list users in Linux using best practices and technical precision. This approach helps maintain system integrity while providing clear, actionable information to technical teams.
FAQ
2. How can I list only the usernames of users in Linux?
To display only usernames, you can use the cut command with "cat /etc/passwd". For example, "cat /etc/passwd | cut -d: -f1" will extract just the usernames from the passwd file, omitting additional details.
3. Are there alternative methods to list users in Linux?
Yes, you can also use "getent passwd" which retrieves user accounts from the system’s name service switch configuration, including local and network users. This method is more comprehensive in environments using LDAP or NIS.
4. How can I distinguish between system users and regular users in Linux?
System users usually have user identifier (UID) numbers lower than 1000, while regular users have UIDs starting from 1000 or higher. By examining the UID field in the "/etc/passwd" file or using awk to filter based on UID, you can separate system from regular users.
5. Is there a way to list currently logged-in users in Linux?
Yes, you can use the who or w commands to display users currently logged into the system. These commands show active sessions and their associated user accounts.
6. How do I display detailed information for a specific Linux user?
To view detailed information about a particular user, use the "id username" command. This will show the user’s UID, group identifier (GID), and group memberships.
7. Can I list user accounts from a remote Linux server?
Yes, you can use SSH to run listing commands remotely. For example, "ssh user@remote-server "cat /etc/passwd"" will list users on the specified remote server, provided you have appropriate permissions.
8. Are there graphical tools for listing users in Linux?
Some graphical desktop environments offer user management tools that display accounts with a graphical interface. However, for most developers and system administrators, command-line methods provide more control and details.
9. How can I ensure the security of the list of users in Linux?
Restrict access to the "/etc/passwd and /etc/shadow" files to prevent unauthorized reading of sensitive user data. Also regularly audit and review user accounts to minimize potential security risks.
10. Why should I regularly review the list of users in Linux?
Regularly reviewing user accounts helps maintain security and system integrity by identifying unused, expired, or unauthorized accounts. It is a best practice for all system administrators maintaining Linux environments.