10 Prevention Solutions for RDP Brute Force Attack
An RDP brute force attack is when cybercriminals try to gain unauthorized access to a computer by systematically guessing the username and password over and over until they find the correct combination.
This kind of attack can lead to serious RDP vulnerabilities, allowing attackers to steal data, install malware, or even take control of the system entirely.
Preventing RDP Brute Force Attacks is critical because a successful breach can have devastating effects, from financial loss to exposing sensitive information.
Some effective strategies include using:
- Strong passwords.
- Enabling two-factor authentication.
- Restricting access to trusted IP addresses.
- Utilizing security tools like RdpGuard.
In the following guide, we will delve deeper into these solutions and more, providing you with the information you need to protect your RDP connections effectively.
1. Finding a Trusted Provider to Use RDP
One effective solution is purchasing RDP from a trusted provider, which often comes with built-in security features that help protect your system.
This option ensures that you are using a service with enhanced security protocols designed to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Use Strong, Complex Passwords
A strong, complex password serves as a critical barrier against RDP brute force attack. Using a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters can make it exponentially harder for attackers to succeed.
It’s also important to update your password periodically to maintain security. There are comprehensive resources available that can guide you with resetting your RDP password.
3. Enable Two-Factor and Multi-Level Authentication (2FA)
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your RDP connection by requiring not just a password, but a second form of verification.
This multi-level authentication can be implemented in various ways to further enhance protection. For instance, you can use authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator to generate time-sensitive codes.
Hardware tokens like YubiKey provide a physical key that must be present to authenticate, while biometric data such as fingerprints or facial recognition adds a highly secure layer of authentication. Push notifications or email-based verification are other options that ensure only legitimate users can access the system.
4. Limit RDP Access to Specific IP Addresses
Restricting RDP access to only trusted IP addresses is a highly effective way to prevent RDP brute force attack.
By limiting who can even try to connect to the RDP server, you cut down on exposure to potential attacks. Configuring your firewall to allow only specific IP ranges will minimize the surface area vulnerable to brute force attempts.
5. Change the Default RDP Port
RDP typically runs on port 3389, which is widely known and frequently targeted by attackers. Changing default RDP port to something less predictable can deter basic brute-force attacks.
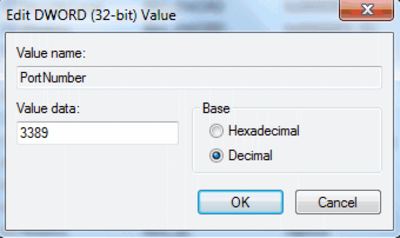
While this won’t stop more sophisticated attackers, it can significantly reduce the likelihood of automated attacks designed to target default ports.
6. Implement Account Lockout Policies
Setting up PDP account lockout policies helps mitigate brute force attacks by temporarily locking accounts after a specified number of failed login attempts. This means that if an attacker fails to log in multiple times, the account will be locked for a certain period or until an administrator unlocks it.
To implement this, you can configure Group Policy settings on Windows servers:
- Open the Group Policy Management Console.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Account Policies > Account Lockout Policy.
Then, set the following policies:
- Specify the number of failed attempts before the account locks.
- Define how long the account remains locked.
- Set the time frame for when the failed attempts counter resets.
7. Use Network Level Authentication (NLA)
Network Level Authentication requires users to authenticate themselves before they can establish a remote session. NLA provides an extra security layer by ensuring that only legitimate users can even begin the RDP process.
By filtering out unauthorized users earlier in the connection sequence, NLA helps to prevent brute force attacks and reduce server load.
8. Use CAPTCHA Code
Integrating CAPTCHA for RDP codes into your RDP login process adds a layer of security by requiring users to complete a challenge that verifies they are human before allowing access. This is particularly effective against automated brute force attacks, as bots typically cannot solve CAPTCHA challenges.
To implement CAPTCHA:
- Choose a service like Google reCAPTCHA or hCaptcha that suits your needs.
- Modify your RDP login screen or the web interface used for remote desktop access to include the CAPTCHA challenge, usually involving adding a few lines of code provided by your chosen service.
- Configure how frequently the CAPTCHA will appear such as after a certain number of failed login attempts to balance user experience with security.
- Finally, test the integration to ensure that the CAPTCHA works correctly and does not impede legitimate users from accessing RDP.
9. Enhance Your Computer’s Security
To ensure your computer remains secure, consider implementing these crucial strategies:
- Activate Your Windows Firewall
Turning on your Windows firewall is essential for safeguarding your computer from unauthorized outgoing connections.
Establishing new rules within the firewall settings can effectively block network-based threats targeting your local machines.
- Keep Your System and Software Updated
Regularly updating your operating system and other software is vital for avoiding vulnerabilities that hackers exploit.
Cybercriminals continuously seek out weak points, so staying current with updates helps defend against viruses and malware.
- Install Antivirus Software
Utilizing reliable antivirus programs is crucial for protecting your computer from malicious attacks.
Connecting via RDP without having antivirus software installed can significantly increase your risk of being compromised by hackers.
- Isolate Outdated and Unsecured Devices
It’s wise to either isolate or replace older computers within your network, as they pose significant security risks.
Legacy hardware can heighten vulnerability to RDP brute force attacks, while outdated systems often provide easy targets for cybercriminals seeking to exploit weaknesses in your network security.
10. Utilize RdpGuard for Enhanced Protection
RdpGuard is a powerful security tool specifically designed to protect your Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connections from brute force attacks.
By monitoring failed login attempts, RdpGuard automatically blocks IP addresses that exhibit suspicious behavior, effectively mitigating the risk of unauthorized access.
This proactive approach not only enhances the security of your RDP sessions but also reduces the workload on your network resources, allowing legitimate users to connect without interruption.
Implementing RdpGuard as part of your security strategy can significantly bolster your defenses against cyber threats.
For more details on how to protect RDP against brute force attacks, refer to Protect RDP Against Brute-Force Attacks using RdpGuard.
That’s it! According to a 2023 report from Cybersecurity Ventures, RDP brute force attack have increased by 300% in the past year as remote work became more common.
Try the explained solutions for RDP Brute Force Attack.
How to understand my RDP is being attacked?
Signs that your RDP might be under attack include:
- Multiple failed login attempts from different IP addresses.
- Unusual account lockouts or user lockouts.
- Sudden changes in network traffic.
- Unrecognized login attempts or access from foreign locations.
What should I do if I suspect an RDP brute force attack?
Immediately change your RDP password, check logs for suspicious activity, and implement additional security measures such as 2FA.
Conclusion
Protecting your RDP connections from brute force attacks is essential for safeguarding your systems and sensitive data.
By implementing strong passwords, limiting access to specific IP addresses, changing the default RDP port, enabling two-factor authentication, setting up account lockout policies, utilizing monitoring tools, and using CAPTCHA codes, you can significantly enhance your RDP security best practices.
Share with us the RDP security measure have you implemented to let others use your real experience.