NVME And SSD Storage Pros and Cons Explained
NVME and SSD storage technologies enhance data storage with faster access and improved efficiency. NVMe offers a high-speed interface for SSDs, greatly reducing latency and boosting performance for demanding tasks.
🤖AI Overview:
NVME And SSD Storage describe solid-state storage solutions where NVMe is a protocol that significantly improves SSD data transfer speeds. NVMe SSDs excel in performance over traditional SSDs, making them ideal for tasks requiring rapid data access and low latency, such as gaming and video editing.
All About NVMe Storage
History will back to the 1970s and 1980s, High-end supercomputers started using SSD-like technology that had first been developed in the 1950s, the technology was prohibitively expensive when it came to storage, and the capacity ranged from 2 to 20 megabytes.
SSD technology was first used in the military and aerospace industries, but it wasn’t until the 1990s that the general public adopted it; SSD prices began to fall in the early 1990s due to technological advancements in storage devices:
The reading and writing time of data in SSD NVMe technology is measured based on nanoseconds; it should be noted that all major operating systems use NVMe technology, first Microsoft in October 2013 for windows operating system 8.1 And then Windows Server R2 2012; after that, Apple added NVMe support to Yosemite 10.10.3 of its operating system and now chrome OS of this technology has benefits.
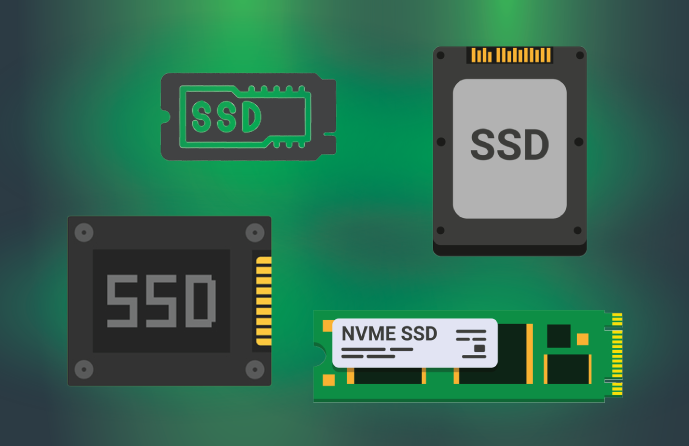
5 Types of SSD Storage
In the following, we will examine the types of SSD Storage to learn more about SSD and NVMe technology than ever before:
- SATA SSD
- PCIe SSD
- M.2 SSD
- U.2 SSD
- NVMe SSD
SATA SSD
SATA SSD is by far the most common type of SSD. SATA (Serial ATA) is the interface that SSDs use to connect to the system and transfer data. Even if your desktop or laptop computer is ten years old, you should be able to use your SATA SSD drive with it.
If you’re looking to buy a solid-state drive, you’ll see SATA 2 and SATA 3 referred to as “SATA II,” or “SATA 3Gbps,” and “SATA III,” or “SATA 6Gbps,” respectively. The drive must be installed in a PC with a SATA interface that supports the same standard to get the maximum data transfer rate.
Since SATA 3.0 can theoretically transfer data at 6Gb/s (750MB/s), it is currently the most versatile form of SSD. However, the actual transfer speed is 4.8Gb/s (600MB/s) due to the physical overhead that occurs during the encoding of the data.
PCIe SSD
An SSD hard drive with a PCIe interface is a PCIe SSD. An SSD connected via PCIe is referred to as a PCIe PCIe PCIe PCIe SSD. Increasing the speed of solid-state drives (SSD) to servers and storage devices has become easier thanks to PCIe SSD.
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe or PCI-e) is the abbreviation for PCI Express. PCIe’s high-speed computer expansion bus standard can replace older bus standards like PCI-X and AGP. Conventional motherboard interfaces for computer graphics cards, hard drive, SSD, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet hardware connections are also PCIe.
M.2 SSD
The M.2 SSD is also a type of SSD. NGFF was the last name (Next Generation Form Factor). Instead of slab-shaped devices, M.2 SSDs are small circuit boards that contain flash memory and controller chips.
Compared to RAM, M.2 SSDs are much smaller and have become a standard configuration in ultra-thin notebook computers, but you can also find them on many desktop motherboards. If you’re using a high-end motherboard, you can even run the M.2 SSD in RAID.
M.2 SSDs come in different lengths and widths, ranging from 80mm to 60mm to 42mm to 22mm, depending on the model, and may have NAND chips on either one or both sides. Four or five digits in the name help you tell it apart from the rest. Width and length are both represented by the first two digits of the number.
M.2 Type-2280 is the most common size. In contrast to laptops, many desktop motherboards have mounting points that can be used for drives of any length.
U.2 SSD
U.2 SSD is an important SSD type to mention. An SSD with a U.2 interface is referred to as a U.2 SSD. The SSD Form Factor Working Group has defined an interface standard known as U.2 (previously SFF-8639) (SFFWG).
Aimed at the enterprise market, U.2 complies with PCI-E, SATA, SATA-E, and SAS interface standard requirements in its development.
U.2 SSDs resemble SATA hard drives in appearance. In contrast to 2.5-inch drives and SSDs, they use a different connector and transmit data over the faster PCIe interface; They are also thicker.
NVMe SSD
SSDs come in various shapes and sizes, each with its unique interface. An SSD with an NVMe interface is called an NVMe SSD or simply an NVMe SSD. Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification is known as NVM Express (NVMe) (NVMHCIS). PCI Express (PCIe) is an open logical device interface specification for accessing non-volatile storage media.
Modern SSDs can utilize NVM Express to utilize all of their parallel processing power. As a result, NVM Express reduces I/O overhead compared to the previous logical device interface and provides various performance improvements, including multiple long command queues and decreased latency. That’s it! These were the 5 Types of SSD Storage that you need to know choosing one for your needs.
Differences between HDD, NVME and SSD Storage!
Let’s see what is the Difference between HDD, SSD, and NVMe Storage. Hard disk drives (HDDs) are electromechanical data storage devices that save and retrieve digital information using one or more disks coated with magnetic material.
For more than half a century, hard disk drives have been steadily improving in terms of storage capacity while simultaneously shrinking in size. Reading and writing data on HDDs is accomplished through the use of spinning disks, also known as platters. Slower than an SSD but cheaper than a mechanical HDD.
The term “solid-state drive” refers to a type of hard drive with no moving parts and, thus, no wear and tear, which is why it performs better than traditional hard drives that have to move and spin parts inside and are mechanical. SSDs are five times faster than a traditional hard disk drive (HDD). There is a 1.5-fold price difference between SSD and HDD.
There are many advantages to using NVMe Storage (Non-Volatility Memory Express) as a new protocol for accessing high-speed storage media over legacy protocols, This interface is designed to meet the requirements of PCI Express solid-state drive-based enterprise and client systems.
Larger file transfers are the only time NVMes come in handy. These drives have a storage capacity that can be seen.
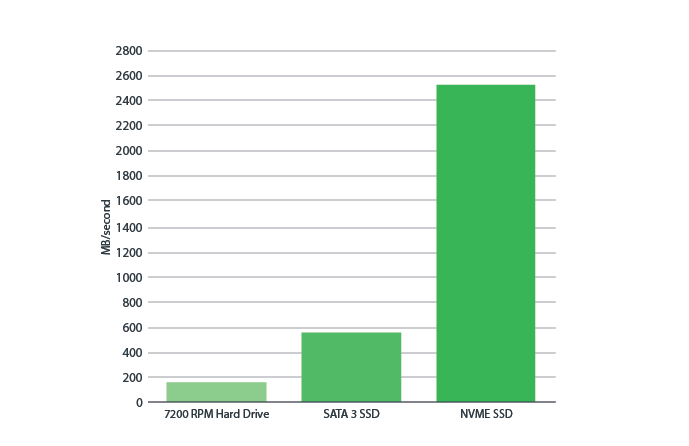
In recent years, storage has undergone a major transformation. Even SATA can’t keep up with NVMe’s blistering speeds. HDDs are more affordable and provide more storage capacity than SSDs. Solid-state drives (SSDs), on the other hand, are a better option in terms of performance, weight, durability, and power consumption. Your specific requirements will determine the best storage drive for you.
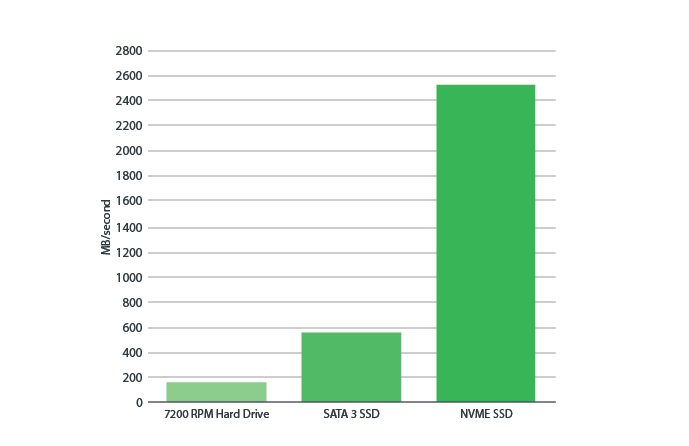
For the most part, a lack of NVMe isn’t worth the extra cost. A good SATA drive is faster than a good NVMe because most applications for which an NVMe would be used are random tasks (i.e., loading a game, booting windows, etc.).
When dealing with extremely large files, NVMe drives are your best bet. If you’re working with high-resolution video and need to edit it quickly, you won’t be using a SATA SSD. Now, if you just want to play games and start Windows, the less expensive option should suffice.
Comparing SSDs And NVMe SSD Storage
Naturally, NVMe will be faster than SSD, which is a new generation of SSD, and can speed up loading or data loading in graphics and other sections; You can see more about the differences between SSD and NVMe through the table below:
| Comparison Parameters | SSD | NVMe |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Solid-State Drive | Non-Volatile Memory express |
| Definition | Integrated circuits store data in SSDs, a type of storage device. As a result, it serves as a backup storage device. | Non-volatile storage can be accessed at high speeds thanks to NVMe, an open logical device interface specification. It's more of a protocol than a hardware component. |
| Speed | An integrated 600 MB per second read/write speed is available. | It can read and write at a rate of 2000 MB per second. |
| Performance | They're slower than NVMe at moving data. | They are 25 times faster than SSDs at transferring data. |
| Efficiency in the use of energy | SSDs use less power than HDDs. | NVMe drives use a lot of power both when running and when they're idle. |
| Security | It is possible to encrypt SSDs. | Compared to SSDs, NVMe Storage is more secure because it uses industry-standard security measures. |
| Affordability | NVMe is more expensive than SSDs. | Costlier than a solid-state drive. |
| Compatibility | Almost any device can use a solid-state drive (SSD). | SATA ports aren't big enough for NVMe, which requires an M.2 port. |
Which Type of SSD is the Fastest?
If you are wondering Which Type of SSD is the Fastest? I must say PCIe SSDs provide three to four times the speed and performance of SATA SSDs in terms of bandwidth, making them the fastest SSDs available. They’re motherboard expansion cards with high-speed interface and performance capabilities that work well with graphics and sound cards.
Expanders, such as PCIe SSDs, allow you to connect additional hardware devices to your computer.
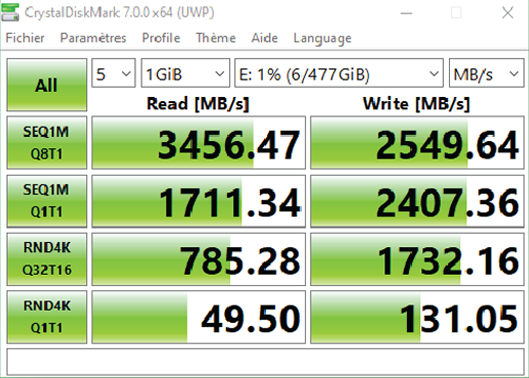
If you’re a gamer, you’ve probably heard of them because you’re always looking for the fastest possible response time, It’s possible to get a PCIe SSD if you don’t mind the price; For obvious reasons, PCIe SSDs are more expensive than SATA SSDs, However, SATA will be your best choice if you need more storage space per performance unit.
Note: You can also view and read another type of post that has already been published about SSD; Difference Between HDD And SSD Server.
Advantages of NVME Storage
You can already see the main advantages of NVME storage below side:
Faster Flash Storage Protocol
Because Apple uses NVMe Storage instead of the Universal Flash Storage (UFS) standard for its flash storage, iPhones and iPads are faster than most Android smartphones and tablets.
Because of its advantages over Embedded MultiMediaCard or eMMC, UFS became a new standard in 2014. When compared, the sequential read and write speeds of UFS 2.0 and EMC 5.1 were both measured at 350 megabytes per second and 150 megabytes per second.
In contrast to eMMC, the Universal Flash Storage can simultaneously read and write to a file on the device. When not in use, it saves twice as much energy as when. External flash drives and laptops’ internal SSD storage soon adopted this standard. The Samsung Galaxy S6 was the first smartphone to use UFS, and it was released in 2015. As a result, other Android device makers followed suit.
Non-Volatile Memory Express, on the other hand, has proven to be a superior flash storage standard to UFS. Solid-state drives made it popular in high-end laptops. Manufacturers prefer this method because it is faster. Apple’s MacBook laptops and top-of-the-line Windows laptops are two good examples.
The iPhone 6S, released in 2015, demonstrated NVMe’s superiority to UFS. Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) connects the device’s internal storage to the NAND. Apple’s iPhone 6S outperformed other flagship smartphones at the time with a sequential read speed of 402 MB/s and sequential write speed of 163 MB/s.
Effectively works with Solid-State Drives
Most solid-state drives use several buses to connect to a computer, such as Serial ATA, Serial Attached SCSI, or Fibre Channel. Because of its benefits over SAS and Fiber Channel, the SATA bus interface has become more widely used and preferred due to the widespread availability of SSDs.
As a matter of fact, like SAS, SATA was primarily designed for hard disk drives (HDDs). The advantages and potentials of using flash memory storage systems were hampered because it is not considered a native interface and a legacy technology for solid-state drives.
NVMe Storage (Non-Volatile Memory Express) was introduced over PCI Express or PCIe to maximize the benefits of solid-state drives. Based on PCIe, it was made from the ground up for NAND solid-state drives. The goal was to introduce a new interfacing protocol for SSDs that would be more efficient to use.
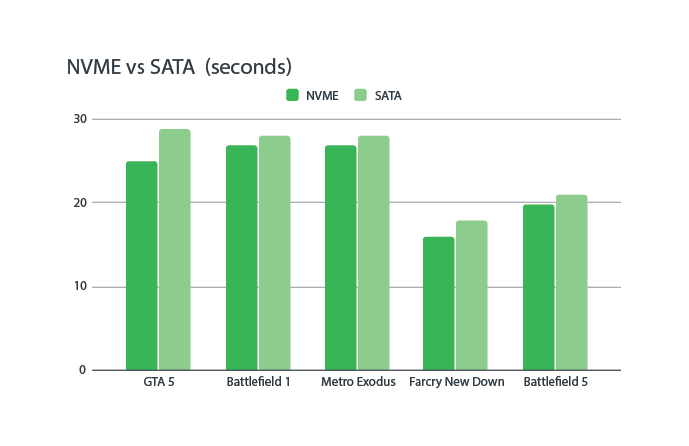
Understanding how Non-Volatile Memory Express differs from SATA is necessary to appreciate its advantages. The SATA protocol serves as a link between flash memory and the computer system, but there are also application layers such as the flash controller, SATA driver, and software RAID in the middle of all of this!
Implementation and Application Flexibility
It’s also possible to get this protocol in various formats. However, U.2 and U.3 add-in card form factors were introduced in response to newer iterations of PCIe and evolving hardware requirements for most early NVMe SSDs.
Note that the M.2 expansion card form factor is a more recent internal mounded expansion technology development. According to the type and functionality of the device, this form factor can be used with either a standard SATA or PCIe interface. M.2 SSDs take up less space and appear cleaner than traditional form factors.
Additionally, the Non-Volatile Memory Express protocol supports a variety of hardware, including internal and external storage on desktops and laptops. It is also very compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and Chrome OS from Google.
With the release of the well-known iPhone 6S, Apple demonstrated that this protocol could be used in mobile devices and mobile operating systems. Of course, a standard solid-state drive (SSD) couldn’t be installed in a smartphone. They modified the protocol when NVMe Storage wasn’t working and built a custom PCIe controller.
VPS Servers With NVME technology
A VPS with an NVMe drive is known as an NVMe VPS server. Virtual private servers offer more adaptability, faster deployment, and lower costs compared to dedicated servers. Using an NVMe VPS server, you’ll be able to take advantage of even faster speeds. Take a closer look at this.
It should be noted that OperaVPS with access to NVMe SSD storage space, various locations, and also equipped with Raid system version 10; Can provide you with quality virtual servers; In order to provide the desired server, you can also refer to the buy VPS, page and activate your desired service❗
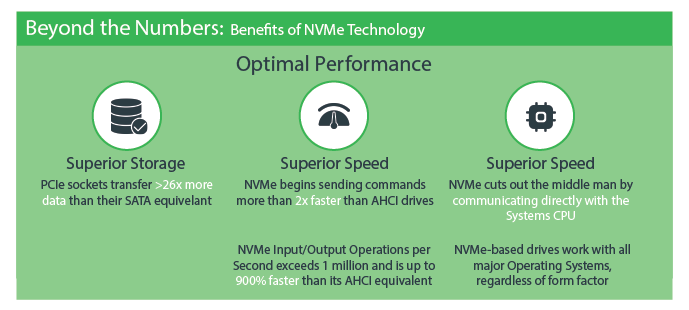
Advantages of Using NVMe VPS Server
- In terms of speed, NVMe is the best option
- Highly Energy-Efficient
- NVMe enables AI systems to deliver more innovation by enabling faster access to data
- Better User Experience
SSD And NVME LifePans
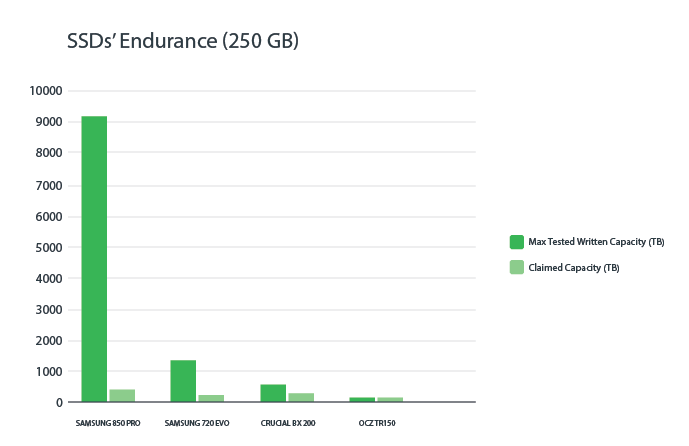
SSD and NVMe Lifespans are originally more than what is predicted; SSDs have a theoretical maximum lifespan of around ten years, but SSDs have a much shorter lifespan in practice. Google and the University of Toronto collaborated on a long-term study of SSDs.
The age of the SSD was found to be the most important factor in determining when an SSD would fail, SSDs were also found to be 25 percent less frequently replaced than HDDs, according to the research.
All About TBW!
What exactly is TBW? Terabytes Written (TBW) is the most common way to express the expected lifespan of a solid-state drive (SSD) (TBW). Because writing data to an SSD affects its lifespan, this is the most important metric. Consumer SSDs have lower TBW ratings than commercial drives, which are more powerful. Higher-capacity drives, such as the 2TB Corsair Force MP600, have TBW ratings of 3600, while most consumer-grade SSDs have TBW ratings no higher than 600. Because we don’t keep track of how much data we’re writing, knowing a drive’s TBW is only useful for comparing different drives.
As with HDDs, the TBW rating may be difficult to locate. It is possible to get conflicting data from various manufacturers. In the case of the WD Black NVMe SSD, which has an MTTF rating of 1.75M hours, the company reports the meantime to failure (MTTF).
In addition, because SSDs are newer, there is less information available about how long they will last. The typical SSD is expected to last ten years under normal usage conditions. That represents an increase over the previous estimate of five to six years.
How long is the lifespan of an NVMe drive? If you buy a 1TB or a 2TB NVMe drive, it may last for up to 800TB or 1200TB. With a 5-year warranty, they also boast a 1.5 million-hour mean time between failures.
When it comes to storage, NVMe is the future, and you should be looking into how you can incorporate it into your current system.SSD and NVMe LifespansSSD and NVMe Lifespans.
Is NVMe worth it?
The main reason why is NVMe storage so expensive? When compared to a SATA-based SSD, they can transfer data 3–5 times faster. This is reflected in the prices. NVMe is the most up-to-date and fastest storage interface for laptops and desktops. As a result, depending on how you intend to use the computer, an NVMe drive may not be a wise investment.
Conclusion
NVME and SSD storage technologies represent a significant advancement in data storage, offering faster performance, lower latency, better reliability, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional hard drives.
While NVME SSDs deliver superior speed and are ideal for intensive tasks, SATA SSDs continue to provide a cost-effective solution for everyday use.
Understanding the differences, types, advantages, and lifespan considerations of NVME and SSD storage will help users make informed decisions tailored to their performance needs and budget.
With the ongoing evolution of these technologies and broader adoption, incorporating NVME and SSD storage into your systems promises a faster, more dependable computing experience.
FAQ
2. What are the main types of SSD storage?
Main SSD types include SATA SSD, PCIe SSD, M.2, U.2, and NVMe SSDs differentiated by interface and form factor.
3. Why is NVMe storage faster than traditional SSDs?
NVMe uses the PCIe bus with multiple command queues and lower overhead, offering faster data transfer.
4. Is NVMe storage suitable for everyday computer use?
NVMe excels in high-performance tasks but SATA SSDs suffice for basic computing needs.
5. How long do NVMe and SSD drives typically last?
Typically, they last around 10 years with lifespan measured by Terabytes Written (TBW).
6. What advantages does NVMe offer over SSDs and HDDs?
NVMe provides faster speeds, lower latency, better energy efficiency, and increased durability.
7. Can I use NVMe SSDs in any computer?
Compatibility depends on motherboard support for M.2 or PCIe slots; check hardware specifications before upgrading.
8. What is an NVMe VPS server and why is it beneficial?
An NVMe VPS uses NVMe SSDs to deliver faster data access and reliability than traditional VPS hosting storage.
9. Are NVMe SSDs worth the cost?
They offer superior performance for data-intensive tasks, though may be unnecessary for basic uses.
10. How does NVMe improve user experience?
By reducing data access times, NVMe enables faster boot times, file transfers, and application responsiveness.
Is nvme storage compatible with older operating systems?
Most modern operating systems that support PCIe-based storage are compatible with NVMe storage. You may need to ensure that the necessary NVMe drive drivers are available for older operating systems.