Learn How to Set the Date and Time on Linux with Ease
It is very important to set the time and date for the server to function properly. In particular, there are services that must be executed and operational on a certain date. Examples of this service are CronJab or Google Autotunitor service, or monitoring services such as Zabbix.
What Is NTP?
With the help of this tool, our computer reads the clock from a source and adjusts its clock based on it. This can be done at adjustable intervals.
The first thing you need to adjust NTP is to find a time server on the Internet or set time linux server if your network is an internal network. Within your network, there are public time servers at the following address.
pool.ntp.orgThe following addresses also include servers that act voluntarily as public NTP servers.
support.ntp.org/bin/view/Servers/WebHomeAfter you have installed NTP on your system using the manager package, the file Open /etc/conf.ntp. This file contains the following lines:
server clock.example.comEach of these lines points to an NTP server. Whenever the NTP daemon is high, it tries to connect to these servers and update the system clock. You can also run the following command to restart this daemon:
# /etc/init.d/ntpd restartTo ensure that NTP is running, you can use the ntpq command which is an interactive application that accepts various commands.
Once you have set up multiple NTP servers, you can configure the NTP client on other computers to point to them. These settings are similar to the settings made on the server. In some cases, an easier way to set the clock on a client is to use the following command:
# ntpdate clock.example.com
example.clock is the NTP server address.
The Timedatectl command allows you to change the system clock configurations as well as its settings. You can use this date command on your system to define or change time and timezone and enable an automatic system clock, which is actually synchronized with NTP Server Remote.
In this article, we’re going to show you how to manage time on your Linux systems by setting the date, time, timezone, and syncing time using NTP and using the new Timedatectl command through the terminal.
How To Find And Define Local Timezone On Linux
You can run the below command to check and time and date on your server:
# timedatectl status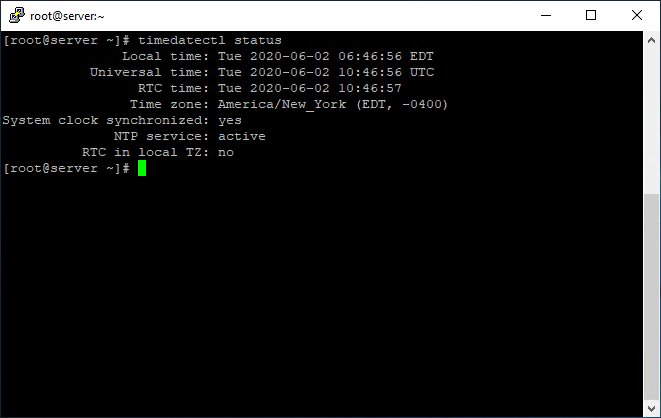
In the image above, RTC time is actually the hardware’s clock time.
How To Set The Date-Time On Linux
You can use the timedatectl command for the Linux date setting.
To set only time, the below command is used in a special format, which is HH: MM: SS (Hour, Minute, and Seconds):
# timedatectl set-time 15:58:30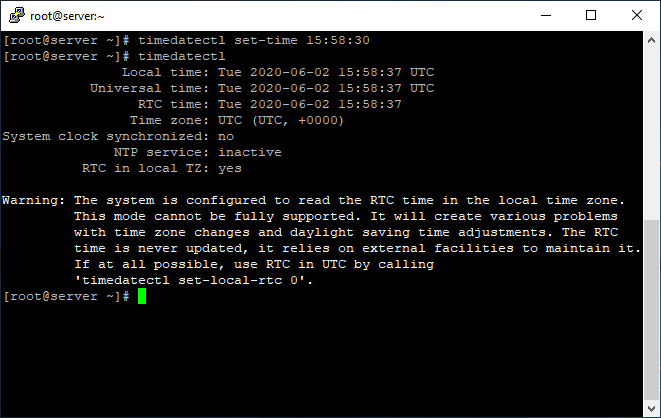
If NTP is active on your server, you face the below error when executing the above command:
Failed to set time: NTP unit is activeIt says that the NTP service is active. You can deactivate it using the below command:
# systemctl disable --now chronydTo set the date only, the set-time option along with the date format in the form of YY: MM: DD (Year, Month, Day) is used:
# timedatectl set-time 2019-04-05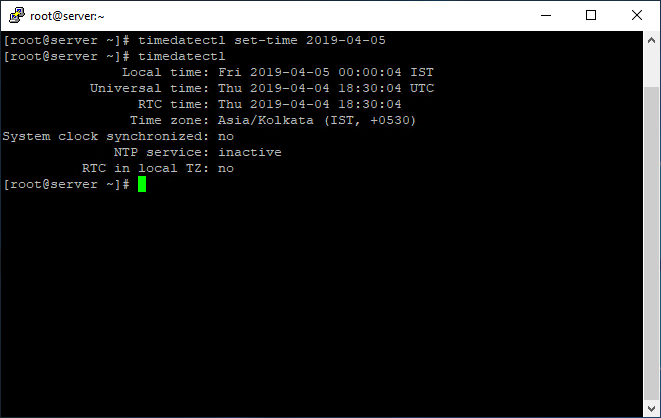
To set the date-time, use the following command:
# timedatectl set-time '16:10:40 2019-11-20'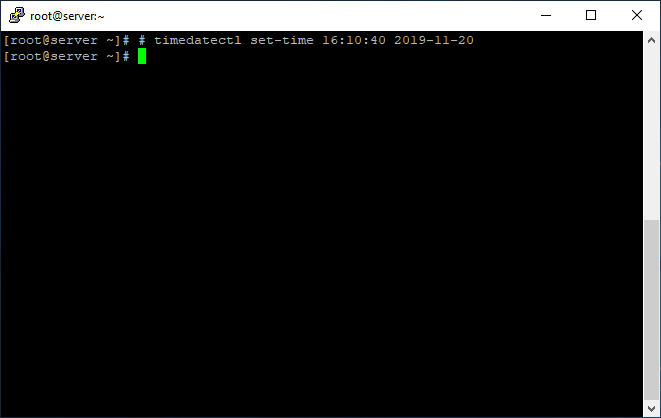
In this article, we have explained very easy examples, and we hope that it will be useful for you and that you can set the date-time and timezone of different Linux VPS systems. To learn more about this tool, visit the Timedatectl man page.
This is quality work regarding the topic! I guess I'll have to bookmark this page.
Do I need superuser privileges for setting date in Linux?
Yes, you need sudo/root privileges to change the system date.
In the first few photos you show the setting for System clock synchronized: set to yes than it changes to no and you do not address how or why you adjusted this setting, than it is changed back to Yes and again its not addressed. How do you toggle this setting from no to yes?
Hi dear Joe. The NTP service manages system clock synchronization, and when this service active, we face an error for setting time/date. To resolve this, we temporarily deactivate it using the command #
systemctl disable --now chronydand enable it again once we set the time, using the command #systemctl enable --now chronyd