
How to Install Nagios on CentOS/ Rocky Linux/ AlmaLinux
Intelligent organizations use monitoring solutions to improve and maintain the application’s performance. As one of the best server monitoring tools, Nagios is designed to run on Linux. Users can easily run it on any operating system. This tutorial is a complete guide to help you install Nagios on CentOS/ Rocky Linux/ AlmaLinux. If you agree that detecting problems before they occur and not facing high costs and downtime is a great idea, join us with this guide and get familiar with Nagios the famous and influential monitoring system, and its installation guidance.
Installing and Using Nagios on your system assists you in monitoring server performance problems and identifying the source of any issue. For those who care about security, Nagios allows you to monitor security concerns and determine whether services are available. In the end, you will be able to use Nagios to change the infrastructure to prevent system failure and monitor different database servers, including SQL Server and MySQL.
Introducing Nagios Monitoring Tool
Nagios is a flexible, free, and open-source server monitoring software. It maintains your networks, servers, apps, and processes operating properly while monitoring your IT infrastructure. Nagios periodically checks key metrics and thresholds to keep an eye out for system changes and potential issues. When a problem occurs with the program, the tool alerts administrators and can also launch automatic scripts to contain and fix the problem.
Both agent-based and agentless server monitoring are supported. You can monitor your servers with more than 5,000 different add-ons that are included. Applications, services, operating systems, network protocols, metrics, and network infrastructure can be monitored with Nagios XI and other mission-critical infrastructure components. Operating systems like Windows, Linux, and Unix can all be watched over using Nagios. Ethan Galstad created Nagios, formerly known as NetSaint, and it was originally made available in 1999. The project was later improved as an open-source project by other contributors. A business built on the Nagios Core technology, The Nagios Enterprise provides several products, including Log Server, XI, Fusion, and Network Analyzer.
There are many monitoring solutions that one can use to monitor your system. Nagios is one of the Top 10 Network Monitoring tools in 2023. In the end, you will be able to install and use Nagios on your Linux operating system.
Tutorial Install Nagios on CentOS/ Rocky Linux/ AlmaLinux
Now that you learned about Nagios, let’s go on this tutorial to review all the required steps to Install Nagios on CentOS, Rocky Linux, and AlmaLinux.
Prerequisites to Install Nagios on CentOS
To let this tutorial work correctly, provide the options below and move on.
- A Server running Linux VPS.
- A non-root user with
sudoprivileges. - Login to CentOS SSH or GUI.
Steps to Install & Use Nagios on CentOS
Using this guide, you can have Nagios on your CentOS to let your complete IT infrastructure be accounted for by Nagios and also make sure your networks, servers, applications, services, and procedures are working smoothly. Nagios uses a variety of mechanisms to transmit notification alerts in the event of failure or subpar performance.
Step 1. Disable SELinux
First, you need to disable SELinux On CentOS. To do this temporarily, run:
$ sudo setenforce 0However, you can disable SELinux permanently. Simply run:
$ sudo sed -i 's/SELINUX=.*/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/configStep 2. Update CentOS Packages
Now, it is time to Update packages and security patches. To do this, run the command below:
$ sudo yum updateStep 3. Install Required Packages
To move on, you need to install prerequisite packages. So, run:
$ sudo yum install gcc glibc glibc-common wget unzip httpd php gd gd-devel perl postfixStep 4. Download Nagios Source File
Use the following commands to download the Nagios source file:
$ cd /usr/src/
$ sudo wget -O nagioscore.tar.gz https://github.com/NagiosEnterprises/nagioscore/archive/nagios-4.4.5.tar.gz
$ sudo tar xzf nagioscore.tar.gzStep 5. Compile Nagios
After a successful download of the Nagios source file, you can run the commands below to compile Nagios on CentOS to make sure all dependencies on your system are available.
$ cd nagioscore-nagios-*/
$ ./configureThen, you can start it by running the following command:
$ sudo make allStep 6. Create Nagios User and Group on Centos
To complete this step, run:
$ sudo make install-groups-usersStep 7: Add Apache User
To the user you created in the previous step, you can add an Apache user by running the command below:
$ sudo usermod -a -G nagios apacheStep 8: Install Nagios Binaries, HTML, and CGIs Files
Run the following command to install Nagios Binaries, HTML, and CGIs files:
$ sudo make installStep 9: Install Daemon and Enable the Service to Start on Boot
To install daemon, run:
$ sudo make install-daemoninitTo enable the service, type:
$ systemctl enable httpd.serviceStep 10. Install Command Mode
To install Command mode, simply run the command below:
$ sudo make install-commandmodeStep 11: Install Sample Config File
To do this step, type:
$ sudo make install-configStep 12: Install Apache Config Files
Use the command below to install Apache Config Files:
$ sudo make install-webconfStep 13: Configure Firewall
In this step, you are ready to configure the firewall and open port 80 for inbound traffic. So, run:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reloadStep 14. Create Nagios Web login user
The command below lets you create a Nagios web login user:
$ sudo htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadminStep 15: Restart the Apache service
At this point, you need to restart Apache. To do this, type:
$ sudo systemctl restart httpdStep 16. Verify Nagios Installation
To confirm Nagios installation, go to your favorite web browser and access Nagios Dashboard: http://<your-centos-ip>/nagios/
Nagios utilizes a server-agent architecture in which the host system’s server is installed along with plugins on the remote system under observation. Through a process scheduler, signals are transferred from the server to the plugins. It is the duty of the plugins to gather the information and deliver it to the scheduler. The process scheduler then refreshes the Nagios GUI and sends the admin the notifications.
From now on, you might face some errors in the hosts tab which can be fixed by installing plugins. The next steps help you to do this.
Step 17. Install Nagios Plugins in Centos
To install Nagios Plugins, you first need some prerequisites:
sudo yum install -y gcc glibc glibc-common make gettext automake autoconf wget openssl-devel net-snmp net-snmp-utils epel-release
sudo yum install -y perl-Net-SNMP18. Download Nagios plugin Source File
Now, you can download the Nagios plugin source file and extract the tar file.
$ cd /usr/src/
$ sudo wget --no-check-certificate -O nagios-plugins.tar.gz https://github.com/nagios-plugins/nagios-plugins/archive/release-2.2.1.tar.gz
$ sudo tar zxf nagios-plugins.tar.gz
$ cd nagios-plugins-release-2.2.1Step 3: Compile and Install Nagios plugin$ sudo ./tools/setup
$ sudo ./configure
$ sudo make
$ sudo make installStep 19. Restart the Nagios Service
It is time to restart your Nagios service. To do this, run:
$ sudo systemctl restart nagios20. Verify Nagios service status
To check if Nagios is running, type:
$ sudo systemctl status nagiosStep 21: Access Nagios Web Interface
To use Nagios on CentOS, you must check if you can access its web interface or not:
http(s)://your_centos_ip_or_domain_or_ip_address/nagios
Then, enter the credentials which you have created in the above steps:
http://add the URL from the above table of contents of step 14
When you go to hosts now, you will see hosts that have been added to the Nagios server and the mentioned issue that has been fixed.
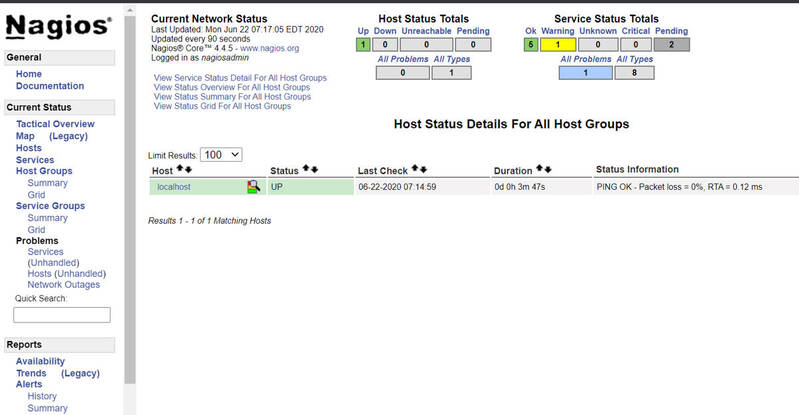
That’s it! You have successfully installed Nagios on CentOS.
Steps to Install Nagios on Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux
Install and Configure Nagios on Rock Linux and AlmaLinux is not that complicated. You just need to follow the below steps to start using Nagios as your network monitoring tool. We assume that after buying Linux VPS, the process of choosing Rocky Linux or AlmaLinux has been finished for you. But if not, the Nagios installation process on both is the same. Just like the prerequisites of installing Nagios on CentOS, keep in mind to consider the non-root user with sudo privileges. If your machine meets all the required specifications, go through the steps of this part to Install Nagios on Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux.
Step 1. Install Required Packages
To get started, run the command below to update all the available packages:
sudo dnf update -yStep 2. Disable SELinux
To set SELinux in permissive mode, run:
sudo sed -i 's/SELINUX=.*/SELINUX=permissive/g' /etc/selinux/config
sudo setenforce 0Step 3. Install Apache Packages
Apache and other build tools are some required packages that can be installed by running the following command:
sudo dnf -y install unzip tar httpd httpd-tools php gcc glibc glibc-common gd gd-devel make net-snmp openssl-develStep 4. Start and Enable Apache
After a successful installation of the above-required packages, use the following command to start and enable Apache and PHP-FPM:
sudo systemctl enable --now httpd php-fpmStep 5. Download Nagios Core Source Code
Go to the Nagios Downloads page to acquire the most recent source code for Nagios Core. As an alternative, you can export the most recent release version by using the command:
NAGIOS_VER=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/NagiosEnterprises/nagioscore/releases/latest|grep tag_name|cut -d '"' -f 4)Once exported, use the following command to download and extract the version:
wget https://assets.nagios.com/downloads/nagioscore/releases/nagios-$VER.tar.gz
curl -SL https://github.com/NagiosEnterprises/nagioscore/releases/download/$NAGIOS_VER/$NAGIOS_VER.tar.gz | tar -xzf -Step 6. Install Nagios Core on Rocky Linux/ AlmaLinux
In this step, you can confirm that all necessary packages have been installed before setting the core to adapt to the system. To do this, run:
cd $NAGIOS_VER
./configureStep 7. Compile Nagios Core
To compile the Nagios core, run:
make allStep 8. Add Nagios User and Group
Run the following command to add a Nagios User and group to the system:
sudo make install-groups-usersStep 9. Add Apache User
To add the Apache user to the Nagios group created, run:
sudo usermod -aG nagios apacheStep 10. Install Nagios Core and init Scripts
To install the Nagios Core, type:
sudo make installUse the command below to install the init scripts for Nagios.
sudo make install-initStep 11. Install Command Mode
Now, you can install the external command file and permissions.
sudo make install-commandmodeStep 12. Install Nagios Configuration Files
To complete this step, type:
sudo make install-configStep 13. Install Apache Configuration Files
Use the following command to install Apache configuration files for Nagios:
sudo make install-webconfStep 14. Install Nagios Plugins in almalinux and rocky linux
The Plugins are used to gather server-side monitoring data. You can install the Nagios Plugins to capture monitoring data from the localhost. Get the most recent source code first from the Nagios Plugins page.
cd ~/
VER=$( curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/nagios-plugins/nagios-plugins/releases/latest|grep tag_name|cut -d '"' -f 4|sed 's/release-//')
curl -SL https://github.com/nagios-plugins/nagios-plugins/releases/download/release-$VER/nagios-plugins-$VER.tar.gz | tar -xzf -Then, go to the directory;
cd nagios-plugins-$VERMake the necessary directory with the correct permissions:
mkdir -p /usr/local/nagios/var/spool/checkresults
sudo chown -R nagios:nagios /usr/local/nagios/var/spool/checkresultsStep 15. Install and Configure Nagios Plugins
To install and configure the plugins of Nagios, run:
./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios
make
sudo make installStep 16. Create the Nagios Web User
We must set up a user account in order to access the Nagios web dashboard. For authentication, this user account will be utilized.
$ sudo htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
New password: PasswordHere
Re-type new password: Repeat_PasswordHere
Adding password for user nagiosadminThe user’s name by default is nagiosadmin. By changing every instance of nagiosadmin in the /usr/local/nagios/etc/cgi.cfg file to the desired username, you can use a different username.
Step 17. Allow Apache to access the configuration file
Set the appropriate ownership and permissions to permit access to the settings file by Apache.
sudo chown apache:apache /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users
sudo chmod 640 /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.usersRestart Apache to make the modifications take effect.
sudo systemctl restart httpdAnd run the following commands to allow the HTTP service through the firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadStep 18. Start and Enable Nagios Service in Rocky linux and Almalinux
To start and enable the Nagios service, type:
sudo systemctl enable nagios --nowThen, reboot the system and check the output for the active (running) line.
sudo reboot nowStep 19. Access the Nagios Web Interface
You can now use the URL http://IP_Address/nagios/ to access the Nagios web UI. You must log in with the nagiosadmin user as displayed.
The dashboard shown below will appear after a successful login.

Congratulations! Now, you are ready to monitor the Memory and disk usage, CPU loads, The number of running processes, Log files, System availability, Response times, URL and content monitoring metrics, and Services and network protocols (SMTP, POP3, HTTP, etc.).
Conclusion
In this article, you learned How to Install Nagios on CentOS, Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux. From now on you can enjoy the continuous monitoring of your system to benefit from constant detecting, reporting, and responding to risks and events within an IT system. Manual monitoring is no longer necessary thanks to Nagios. Additionally, Nagios centralizes and standardizes monitoring for all environments, gadgets, and systems.
If you follow the above steps of each part properly, you can smoothly install Nagios on your operating system without any errors but do not hesitate to contact us if you encounter any problems. Our technical support team will try their best to solve your problems.