Git for Beginners Easy Guide to Get Started
Git is a version control system that helps you track changes in code and collaborate with others. Beginners use Git to manage projects and restore previous versions easily.
🤖AI Overview:
Git is a widely used version control system designed to track changes in source code during software development. Its main purpose is to help multiple people collaborate on projects while keeping a detailed record of every modification. Git allows developers to easily manage and merge code changes, greatly reducing the risk of conflicts or data loss. This makes git essential for teams needing reliable and efficient project coordination.
Quick Steps
- Install git using your Linux package manager or download from the official website.
- Confirm installation by typing git
--versionin the terminal. - Set your username and email with
git config --global user.nameandgit config --globaluser.email. - Create a new project folder and run
git initto start tracking. - Add files to your project using git add filename or git add .
- Save your changes with
git commit -m "your message". - Check file status anytime with git status.
- Clone an existing project with git clone and the repository URL.
Introduction to Git?
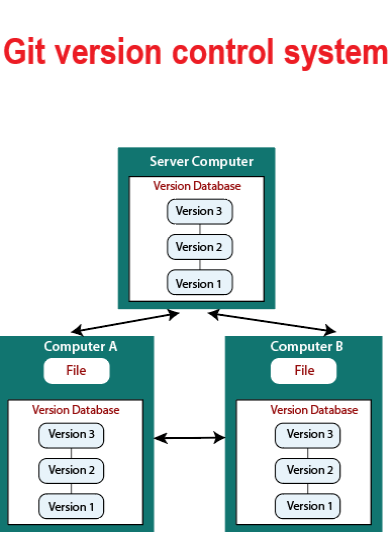
Git is a free and open-source distributed version control system. Both small and very large projects are handled by Git with speed and efficiency. Git is really fast to perform all operations locally. Centralized systems that have to communicate with a server somewhere constantly, will appreciate the huge speed of Git. Enabling multiple developers to work together on non-linear development, Git tracks changes in source code.
To find the best way to manage various code versions, let’s go through this article and see how to merge them with the main code after testing.

What is VCS and how it works?
VCS is the abbreviation of the version control system. As a developer, you can use the version control system (VCS) to track file changes. Various versions of files and changes made to each version are created by VCS. In this way, you will be able to switch between various versions of the files seamlessly. By storing a collection of file changes on the repository, it helps track changes in source code files. A version control system can track changes in binary data, not just text files.
There are various types of version control systems such as:
- Localized Version control systems
- Centralized version control system
- Distributed Version control system
Git Features
Using Git enables you to not submit your codes to the central server without having copies of your own. Once you install Git, all changes made to the source code will be known, and you can communicate with other developers. Here is more:
- Free and open source
- Frictionless Context Switching
- Supports non-linear development
- Distributed development
- Tracks history
- Role-Based Code lines
- Branching is easier
- Creates backups
- Feature Based Workflow
- Supports collaboration
- Scalable
- Disposable Experimentation
- Distributed development
Head over to the Git Community to find any reported issues quoted from users and see what also are downsides of Git are.
Prerequisites to install Git on Linux
Before tracing the installation steps on this guide, make sure you are logged in as root or a user with sudo privileges.
Git Installation on Linux
Git should have been installed on your operating system with all the major Linux distributions. But depending on the system you are using, it may not be installed. Git packages are available via apt. So, run the command below on your system.
Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y sudo apt-get install git -yArch Linux
sudo pacman -S GitFedora/Red Hat/CentOS
sudo yum install git
sudo dnf install git
To verify that if the installation was successful, type:
$ git --versiongit version 2.9.2How to build Git from source on Linux?
To build on Linux, Git requires several dependencies. To make them available. Run:
$ sudo apt-get update$ sudo apt-get install libcurl4-gnutls-dev libexpat1-dev gettext libz-dev libssl-dev asciidoc xmlto docbook2xNow, use the command below to clone the Git source.
$ git clone https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/git/git.gitThen, type the following command to build Git and install it under /usr, run make :
$ make all doc info prefix=/usr$ sudo make install install-doc install-html install-info install-man prefix=/usrHow to Configuration Git on Linux?
After a successful installation, you are ready to access and use all Git’s commands working with local and remote repositories. First-time use needs a configuration. Running the below command allows you to configure your Git username and email address, and the default text editor.
Note: Replace OperaVPS with your own.
$ git config --global user.name "OperaVPS"$ git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
git config --global core.editor vim
Then, use the following command to view the git configuration.
git config --list
user.name=myusername
[email protected]
core.editor=vim
How to Set up/Use Git repositories on Linux?
Files and directories are collected in the repository with their respective changes tracked by the version control system. Commits manage or tracking changes in a repository. Using commits allows you to apply the changes or revert to a specific change within the repository.
In the case of having a project directory, you can initialize it using the command below to use as a git repo and track changes. Then, Git will initialize the directory as a repository and creates a .git directory used to store all the configuration files.
git initNow, type the following command to start tracking changes. For example, to add the file, reboot.c:
git add reboot.cNow you can add the files in that directory and start tracking changes if you run the command below:
git add .To add the message (file) indicating the changes to the files, just use something like the following command:
git commit -m “Initial Commit.”Clone a remote repository
It is possible to work with remote repositories. Cloning is to copy all the files in a remote repo to the local repo. So, type:
git clone https://github.com/linuxhint/code.gitRun the command below to view the status of the files in the repository.
git statusObviously, after running the command above, you will see whether the files in the repository are changed or not.
Also, you can get all the changes from the remote repository and merge them into the local one. When you have a clone repository, run the following command to update the local repo from the remote.
git fetchCreate and Delete a remote repository
Use the following command to create a new remote repository.
git remote add new_repo https://github.com/operavps/new_repo.gitAlso, whenever you wish to delete a remote repository from the command line, type:
git remote rm https://github.com/operavps/new_repo.gitThat’s It! Just start working with local and remote repositories.
FAQ
3. What are the basic Git commands every beginner should know?
As a beginner, you should start with these Git commands: git init to create a new repository, git clone to copy an existing repository, git add to stage changes, git commit to save changes, git status to check your repository state, and git push to upload changes to a remote server.
4. How can I set up my name and email in Git?
Setting up your name and email in Git is important for recording who made changes. Use these commands in your terminal: git config --global user.name "Your Name" and git config --global user.email "[email protected]". This ensures your future commits are properly attributed.
5. What is a Git repository, and how do I create one?
A Git repository is a place where your project files and their change history are stored. To create a new repository, go to your project directory in the terminal and type git init. This sets up Git tracking for your project.
6. How does Git help in managing different versions of my project?
Git keeps a detailed history of every change to your files. You can view earlier versions, switch back if needed, and work on new features without affecting the main project. This makes it safe and easy to experiment or fix problems.
7. What does it mean to commit changes in Git?
Committing changes in Git means saving a snapshot of your files at a given moment. Each commit records what changed, when, and who made the change. This is important for tracking your work and undoing mistakes.
8. How do I fix a mistake or undo changes in Git?
If you want to undo changes, Git offers several options. You can use git checkout to restore files, git revert to undo specific commits, or git reset to change your commit history. Each command serves a different scenario, so it is important to learn when to use each.
9. What is the difference between Git and other version control systems?
Git is a distributed version control system, which means every user has a complete copy of the project history. Compared to older systems like SVN or CVS, Git is faster, more flexible, and better suited for collaborative work, especially for open-source projects.
10. Where can I learn more about Git and improve my skills?
There are many free resources online, such as the official Git documentation, interactive tutorials, and beginner-friendly video guides. Joining forums and community groups can also help you solve problems and learn from others.
Conclusion
Learning git step by step will build your confidence in version control. Each of these stages plays an important role in organizing and protecting your work. I encourage you to practice these steps and explore more about git as you continue your journey. If you have questions, feel free to seek support. Happy coding from Ashley B. at OperaVPS!