Understanding TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
TCP, or Transmission Control Protocol, ensures reliable and ordered data transfer over networks by breaking data into packets, sending them, and reassembling them accurately at the destination.
🤖AI Overview:
TCP is a fundamental Internet protocol that manages the reliable transmission of data between devices. It divides messages into packets, maintains the correct order, and confirms delivery through connection establishment and error checking. TCP is vital for applications needing consistent and error-free communications.
What is Internet Protocol (IP)?
The Internet Protocol, or IP, is a set of rules for routing data on the Internet to reach the correct destination.
Every computer, phone, or other machine that connects to the Internet is assigned an IP address so that data can reach its accurate destination.
How Transmission Control Protocol works?
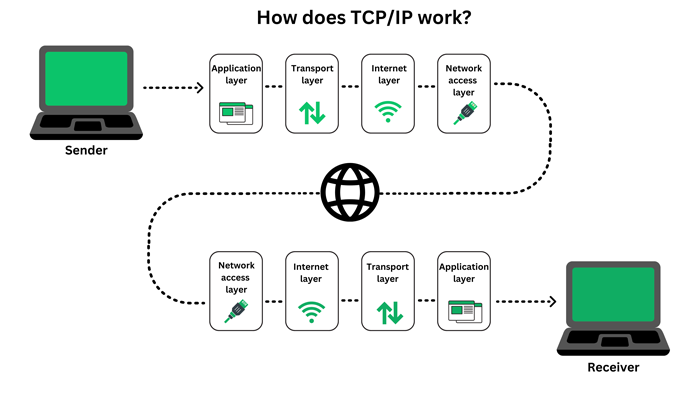
The default method of communicating data on the Internet is TCP/IP protocol.
First of all, It is crucial to mention that the messages sent through TCP/IP are not private and can be seen. For this reason, it’s better to use a VPN or VPS.
The TCP protocol divides the message into smaller packets to facilitate its traversal through the Internet. The packets can travel between the sender and the receiver through different routes if the initial route is blocked. When the message is received, the TCP/IP protocol on the destination side reassembles the packets to the original message.
Are TCP and IP the same?
No, The TCP and IP are distinct Internet protocols. Their role in the transmission process differs.
The IP protocol obtains the destination address (IP), and the TCP protocol ensures the message is sent to the exact provided (IP) address.
For clarification, we can say that the IP is similar to the phone numbers, while TCP is the technology that enables us to talk with each other on the phone.
Why is TCP used?
TCP is like a reliable postal service for data traveling between a server and a client. It ensures that the data sent over the Internet stays intact and arrives safely.
It’s commonly used to handle data for higher-level protocols that need all their information to reach their destination without any issues.
layers of TCP/IP
The TCP/IP protocol, which is also used in VPN, sends the data to its layers to transmit it.
These layers handle the rest of the work independently of any hardware or software.
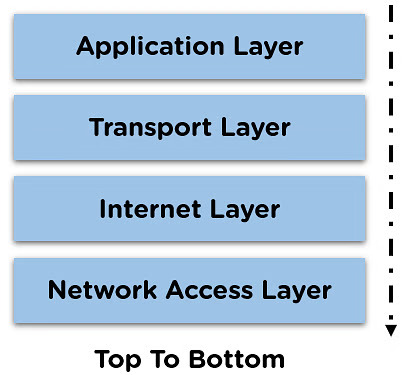
The TCP/IP has four layers (top to bottom):
- Application layer
This is the layer with which the end user interacts and can use to access the Internet. - Transport layer
This layer has the duty of dividing the message and ensuring that the receiver understands the received messages. - Internet layer
This layer reassembles the message in the correct order so the end user can understand it. - Network Access layer
The lowest layer, or the Network Access Layer, holds the protocols that computers use to communicate with other computers and devices connected to the network.
Features of TCP protocol
Here are some notable features of the TCP/IP protocol listed:
- Congestion Control:
The congestion level matters to TCP/IP. The TCP/IP controls the congestion level based on the size of the sent data. - Full Duplex:
The TCP/IP protocol can send and receive messages simultaneously, speeding up data transfer. - Error Control:
TCP/IP checks the packets for any errors, such as lost or corrupted packets, before reassembling them to the original message. - Segment Numbering System:
Each transferred packet is assigned a number. This way, the TCP/IP keeps track of each segment of the message. - Connection Oriented:
TCP/IP needs a connection to send and receive messages successfully.
Advantages of TCP/IP
If you wonder what the advantages of the TCP/IP model are, here you go:
- It is a reliable protocol which has error detection and resends packets if lost
- This protocol is an open one, and no company owns it
- It uses flow control to prevent sending too much data at a time
- TCP sends and receives packets in the initial order
- It supports various routing protocols
Disadvantage of TCP/IP
- It is connection-oriented, meaning that the data transfer will be stopped if the connection is dropped
- TCP/IP’s overhead is more than UDP‘s
- All the data must be received before it starts to reassemble and reload them
- In relation to network congestion, TCP/IP will reduce the transfer rate
- It does not support multicast or broadcast transmission
What is a three-way handshake in TCP/IP?
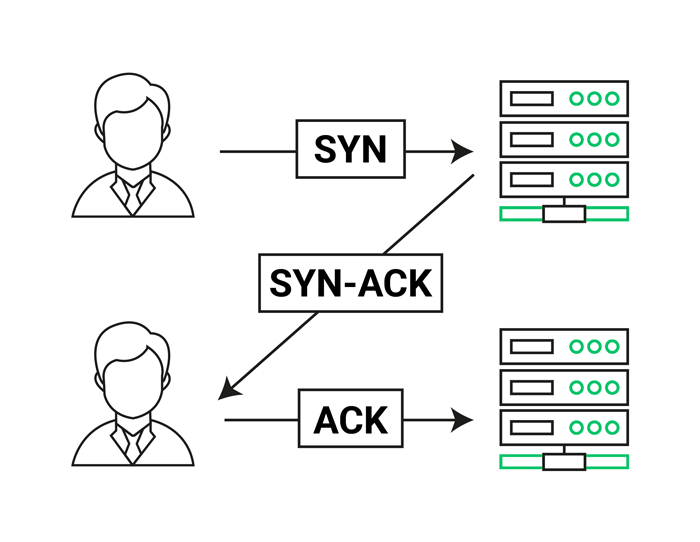
The TCP/IP model establishes a dependable connection through a process known as a three-step agreement.
This connection allows for simultaneous two-way communication, with both ends coordinating by sending synchronization (SYN) and acknowledgment (ACK) signals.
The synchronization and acknowledgment flags are interchanged in a sequence of three stages:
- SYN
- SYN-ACK
- ACK
Why use TCP in VPNs?
TCP implements error-checking and retransmission mechanisms to ensure complete data transfer. Additionally, TCP/IP translates the message in the order in which it was sent.
If you want your messages to be sent and received successfully, the TCP/IP is the ideal choice.
Furthermore, on some occasions, UDP connections are not allowed, and VPNs use TCP to establish secure connections.
Why not use TCP in VPNs?
Implementing TCP/IP in VPNs can cause a problem called “TCP Meltdown”.
When a VPN employs TCP, it essentially layers one TCP/IP model on top of another on the user’s device, which should technically be more reliable.
However, if a packet is lost, both the VPN’s TCP/IP protocol and the user’s TCP attempt to resend it, causing potential packet overflow leading to a TCP Meltdown.
This continuous retransmission cycle can result in communication failure and data loss. Alternative protocols like UDP are being considered for VPN protocol use to address this issue.
How is TCP used in VPNs?
A VPN works like a secret tunnel on your device using TCP/IP routing algorithms.
This tunnel connects you to the VPN server, giving you a new IP address. Whenever you send or receive data, it zips through this special tunnel instead of the regular path.
This tunneling ensures that your data is kept safe and private as it makes its way to the VPN server.
The server then determines where your data needs to go using its own algorithms (like TCP/IP or UDP).
When data is sent back to you, it goes through the same process, getting encrypted by the VPN server before reaching your device and applications.
What is the OSI model?
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model enables various devices to communicate with each other on a network.
Communication takes place using numerous protocols. We can say that the OSI model is a global language for computers.
The OSI model has seven layers. Each of these layers has its unique job and communicates with the upper and lower layers.
The layers from top to bottom are:
- The application layer
- The presentation layer
- The session layer
- The transport layer (TCP and UDP protocols are included in this layer)
- The network layer
- The data link layer
- The physical layer
OSI vs. TCP
1. The first difference between the TCP/IP and OSI models is their number of layers. The TCP/IP model has four layers, while the OSI model has seven layers. These layers correspond to different layers of the other model.
2. When comparing the two reference models, the OSI model is exclusively a conceptual framework. Its primary role is to delineate and comprehend specific network functionalities.
3. TCP/IP focuses on addressing particular issues rather than serving as an all-encompassing blueprint for network communication.
4. The OSI model is general and not tied to any protocol, yet most systems and protocols conform to its principles, whereas the TCP/IP model relies on standard Internet protocols.
5. Additionally, the OSI model allows for flexibility in simpler applications by not mandating the use of all layers.
TCP vs. UDP
Here are the main differences between TCP and UDP protocols:
| TCP | UDP |
|---|---|
| A bit slower | Fast |
| More reliable | Reliable |
| Used for file transfer, web browsing and emails | Used for online gaming, live streams and VOIP |
| Unicast | Unicast, multicast, broadcast |
| Connection-oriented | Connectionless |
| Checks for errors | Does not check for errors |
| Guarantees message delivery | Does not guaranty message delivery |
| Sends messages in a fixed sequence | Does not have any particular order |
| Uses flow control | Does not use flow control |
| Implements control congestion | Does not implement control congestion |
| Has longer headers | Has shorter headers |
| Higher overhead | Lower overhead |
Which protocol is better: TCP or UDP?
The right answer to this question entirely depends on what you intend to do with these protocols.
TCP is the best option for secure and guaranteed data delivery, while UDP is the best option for broadcast-based activities.
For example, UDP is best for online gaming and live streams, while TCP is best for messaging or file transfer.
Overall, the action you want to do online determines which protocol you should use.
UDP is better for:
- Online gaming
- Streaming
- Video chat
TCP is better for:
- File transfer
- Email and text messaging
- Web browsing
Conclusion
TCP is a vital protocol in modern networking that ensures reliable, ordered, and error-free data transmission over the internet. Its combination with IP allows devices to address, route, and deliver data packets efficiently. TCP’s layered architecture, key features like congestion control and error correction, and its implementation in critical technologies such as VPNs highlight its importance. Understanding TCP alongside other models and protocols like OSI and UDP helps clarify how internet communication functions and guides the best practices for network design and application development. When stability and data accuracy are priorities, TCP remains the protocol of choice.
FAQ
TCP and IP are different protocols where IP obtains the destination address for data routing, while TCP ensures the data is delivered accurately and in the correct order to that address. TCP works by breaking data into smaller packets, sending them through the internet possibly via different routes, and reassembling them at the destination. It also performs error checking to ensure data integrity. TCP is used in VPNs because it provides error checking and retransmission capabilities, ensuring complete and ordered data transfer through the encrypted tunnel between the user and the VPN server. Key advantages of TCP include reliable data delivery through error detection and retransmission, flow control to manage data transfer rates, and maintaining the correct order of packets. TCP can slow down data transfer due to its connection-oriented nature, overhead from error checking, and it does not support multicast or broadcast transmissions. TCP guarantees reliable and ordered delivery of data, making it suitable for tasks like file transfer and web browsing. UDP is faster but less reliable, used mainly for applications like online gaming and live streaming. The three-way handshake is a process used by TCP to establish a reliable connection between client and server involving synchronization and acknowledgment steps before data transmission begins. TCP manages network congestion by adjusting the rate of data transmission based on current network traffic conditions to prevent packet loss and ensure smooth communication. TCP is preferred when data accuracy and reliability are critical, such as in email, file transfers, and web browsing, because it ensures data packets are correctly sent, received, and ordered. 2. How does TCP differ from IP?
3. How does the TCP protocol work?
4. Why is TCP important in VPNs?
5. What are the main advantages of using TCP?
6. What are the disadvantages of the TCP protocol?
7. What is the difference between TCP and UDP?
8. What is a three-way handshake in TCP?
9. How does TCP control congestion in networks?
10. Why should TCP be chosen over other protocols?